Clinical characteristics, pathological distribution, and prognostic factors in non-Hodgkin lymphoma of Waldeyer's ring: nationwide Korean study
- PMID: 24851070
- PMCID: PMC4028525
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2014.29.3.352
Clinical characteristics, pathological distribution, and prognostic factors in non-Hodgkin lymphoma of Waldeyer's ring: nationwide Korean study
Abstract
Background/aims: In Asia, the incidence of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) has increased in recent decades. Waldeyer's ring (WR) is the most common site of NHL involving the head and neck. In this study, the pathological distribution of WR-NHL and its clinical features were analyzed retrospectively.
Methods: From January 2000 through December 2010, we analyzed the medical records of 328 patients from nine Korean institutions who were diagnosed with WR-NHL.
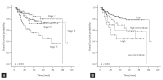
Results: The study group comprised 197 male and 131 female patients with a median age of 58 years (range, 14 to 89). The rate of localized disease (stage I/II) was 64.9%, and that of low-risk disease (low/low-intermediate, as defined by the International Prognostic Index) was 76.8%. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL; 240 patients, 73.2%) was the most common pathologic subtype, followed by peripheral T-cell lymphoma (14 patients, 4.3%) and nasal NK/T-cell lymphoma (14 patients, 4.3%). WR-NHL occurred most frequently in the tonsils (199 patients, 60.6%). Extranodal involvement was greater with the T-cell subtype (20 patients, 42.5%) compared with the B-cell subtype (69 patients, 24.5%). Multivariate analyses showed that age ≥ 62 years, T-cell subtype, and failure to achieve complete remission were significant risk factors for overall survival.
Conclusions: DLBCL was found to have a higher incidence in Korea than those incidences reported by other WR-NHL studies. T-cell lymphoma occurred more frequently than did follicular lymphoma. T-cell subtype, age ≥ 62 years, and complete remission failure after first-line treatment were significant poor prognostic factors for overall survival according to the multivariate analysis.
Keywords: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; Head and neck; Non-Hodgkin lymphoma; T-cell lymphoma.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Waldeyer's ring lymphomas: a clinical study from the Comprehensive Cancer Center West population based NHL registry.Leuk Lymphoma. 2001 Sep-Oct;42(5):1005-13. doi: 10.3109/10428190109097720. Leuk Lymphoma. 2001. PMID: 11697617
-
Localized non-Hodgkin's lymphoma of Waldeyer's ring: clinical features, management, and prognosis of 130 adult patients.Head Neck. 2001 Jul;23(7):547-58. doi: 10.1002/hed.1077. Head Neck. 2001. PMID: 11400243
-
Clinical characteristics and prognostic analysis of primary extranodal non-Hodgkin lymphoma of the head and neck.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Apr 5;16(8):6796-6808. doi: 10.18632/aging.205726. Epub 2024 Apr 5. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38604163 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma of the Waldeyer's ring: clinicopathologic and therapeutic issues.Leuk Lymphoma. 2008 Dec;49(12):2263-71. doi: 10.1080/10428190802493686. Leuk Lymphoma. 2008. PMID: 19052973 Review.
-
Hodgkin lymphoma involving extranodal sites in head and neck: report of twenty-nine cases and review of three-hundred and fifty-seven cases.Hematology. 2021 Dec;26(1):103-110. doi: 10.1080/16078454.2020.1865667. Hematology. 2021. PMID: 33478377 Review.
Cited by
-
Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Parameters and D-Dimer: New Prognostic Parameters for Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma.Cancer Manag Res. 2022 Aug 26;14:2535-2544. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S326173. eCollection 2022. Cancer Manag Res. 2022. PMID: 36051181 Free PMC article.
-
Pattern of bone marrow involvement in non Hodgkin's lymphoma classified according to WHO classification: Report of a developing country Pakistan.J Lab Physicians. 2018 Jan-Mar;10(1):17-20. doi: 10.4103/JLP.JLP_9_17. J Lab Physicians. 2018. PMID: 29403198 Free PMC article.
-
[Dual epigenetic therapy in TET2 gene positive extranodal peripheral T-cell lymphoma with follicular helper T-cell (TFH) phenotype: a case report and literature review].Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2023 Jul 14;44(7):590-593. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-2727.2023.07.013. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37749042 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese. No abstract available.
-
MRI of diffuse large B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma of the head and neck: comparison of Waldeyer's ring and sinonasal lymphoma.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2017 Feb;274(2):1079-1087. doi: 10.1007/s00405-016-4337-2. Epub 2016 Oct 13. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2017. PMID: 27738821
-
Role of radiation therapy in primary tonsil large B cell lymphoma: a SEER-based analysis.Radiat Oncol. 2021 Oct 2;16(1):193. doi: 10.1186/s13014-021-01919-x. Radiat Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34600539 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:2893–2917. - PubMed
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. - PubMed
-
- Baris D, Zahm SH. Epidemiology of lymphomas. Curr Opin Oncol. 2000;12:383–394. - PubMed
-
- Weisenburger DD. Epidemiology of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: recent findings regarding an emerging epidemic. Ann Oncol. 1994;5(Suppl 1):19–24. - PubMed
-
- Hoppe RT, Burke JS, Glatstein E, Kaplan HS. Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: involvement of Waldeyer's ring. Cancer. 1978;42:1096–1104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
