Effects of Brilliant Blue G on Serum Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Levels and Depression-like Behavior in Mice after Lipopolysaccharide Administration
- PMID: 24851118
- PMCID: PMC4022763
- DOI: 10.9758/cpn.2014.12.1.31
Effects of Brilliant Blue G on Serum Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Levels and Depression-like Behavior in Mice after Lipopolysaccharide Administration
Abstract
Objective: Accumulating evidence suggests that inflammation plays a role in the pathophysiology of major depression. The adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-sensitive P2X7 receptor (P2X7R) plays a crucial role in microglial activation caused by inflammation. The dye brilliant blue G (BBG) is a P2X7R antagonist. This study examined whether BBG shows antidepressant effects in an inflammation-induced model of depression.
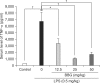
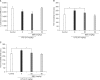
Methods: We examined the effects of BBG (12.5, 25, or 50 mg/kg) on serum tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) levels after administering the bacterial endotoxin lipopolysaccharide (LPS; 0.5 mg/kg) and the effects of BBG (50 mg/kg) on depression-like behavior in the tail-suspension test (TST) and forced swimming test (FST).
Results: Pretreatment with BBG (12.5, 25, or 50 mg/kg) significantly blocked the increase in serum TNF-α levels after a single dose of LPS (0.5 mg/kg). Furthermore, BBG (50 mg/kg) significantly attenuated the increase in immobility time in the TST and FST after LPS (0.5 mg/kg) administration.
Conclusion: The results suggest that BBG has anti-inflammatory and antidepressant effects in mice after LPS administration. Therefore, P2X7R antagonists are potential therapeutic drugs for inflammation-related major depression.
Keywords: Coomassie Brilliant Blue; Cytokine; Depression; Inflammation; Purinergic P2X7 receptors; Tumor necrosis factor-alpha.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of amycenone on serum levels of tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-10, and depression-like behavior in mice after lipopolysaccharide administration.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2015 Sep;136:7-12. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2015.06.012. Epub 2015 Jul 4. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2015. PMID: 26150007
-
Effects of escitalopram, R-citalopram, and reboxetine on serum levels of tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-10, and depression-like behavior in mice after lipopolysaccharide administration.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2016 May;144:7-12. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2016.02.005. Epub 2016 Feb 15. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2016. PMID: 26892759
-
Antidepressant-like Effects Induced by Chronic Blockade of the Purinergic 2X7 Receptor through Inhibition of Non-like Receptor Protein 1 Inflammasome in Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress Model of Depression in Rats.Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2019 May 31;17(2):261-272. doi: 10.9758/cpn.2019.17.2.261. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30905126 Free PMC article.
-
A P2X7 receptor antagonist reverses behavioural alterations, microglial activation and neuroendocrine dysregulation in an unpredictable chronic mild stress (UCMS) model of depression in mice.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2018 Nov;97:120-130. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2018.07.016. Epub 2018 Jul 10. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2018. PMID: 30015007
-
Effects of Jiaotaiwan on depressive-like behavior in mice after lipopolysaccharide administration.Metab Brain Dis. 2017 Apr;32(2):415-426. doi: 10.1007/s11011-016-9925-8. Epub 2016 Oct 30. Metab Brain Dis. 2017. PMID: 27796565
Cited by
-
P2X7 receptor contributes to long-term neuroinflammation and cognitive impairment in sepsis-surviving mice.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Apr 21;14:1179723. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1179723. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37153798 Free PMC article.
-
Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF)-TrkB Signaling in Inflammation-related Depression and Potential Therapeutic Targets.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2016;14(7):721-31. doi: 10.2174/1570159x14666160119094646. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26786147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanistic insights into the anti-depressant effect of curcumin based on network pharmacology and experimental validation.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Jan;397(1):583-598. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02628-w. Epub 2023 Jul 25. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37490124
-
The Gut-Brain Axis: The Missing Link in Depression.Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2015 Dec 31;13(3):239-44. doi: 10.9758/cpn.2015.13.3.239. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26598580 Free PMC article.
-
The rapid antidepressant effect of ketamine in rats is associated with down-regulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the hippocampus.Ups J Med Sci. 2015;120(4):241-8. doi: 10.3109/03009734.2015.1060281. Epub 2015 Jul 28. Ups J Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 26220286 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hashimoto K. Emerging role of glutamate in the pathophysiology of major depressive disorder. Brain Res Rev. 2009;61:105–123. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

