Reliability of stereotactic coordinates of 1.5-tesla and 3-tesla MRI in radiosurgery and functional neurosurgery
- PMID: 24851148
- PMCID: PMC4024812
- DOI: 10.3340/jkns.2014.55.3.136
Reliability of stereotactic coordinates of 1.5-tesla and 3-tesla MRI in radiosurgery and functional neurosurgery
Abstract
Objective: The aims of this study are to identify interpersonal differences in defining coordinates and to figure out the degree of distortion of the MRI and compare the accuracy between CT, 1.5-tesla (T) and 3.0T MRI.
Methods: We compared coordinates in the CT images defined by 2 neurosurgeons. We also calculated the errors of 1.5T MRI and those of 3.0T. We compared the errors of the 1.5T with those of the 3.0T. In addition, we compared the errors in each sequence and in each axis.
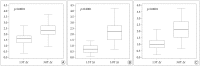
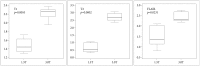
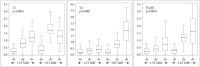
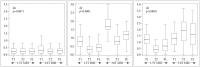
Results: The mean difference in the CT images between the two neurosurgeons was 0.48±0.22 mm. The mean errors of the 1.5T were 1.55±0.48 mm (T1), 0.75±0.38 (T2), and 1.07±0.57 (FLAIR) and those of the 3.0T were 2.35±0.53 (T1), 2.18±0.76 (T2), and 2.16±0.77 (FLAIR). The smallest mean errors out of all the axes were in the x axis : 0.28-0.34 (1.5T) and 0.31-0.52 (3.0T). The smallest errors out of all the MRI sequences were in the T2 : 0.29-0.58 (1.5T) and 0.31-1.85 (3.0T).
Conclusion: There was no interpersonal difference in running the Gamma Plan® to define coordinates. The errors of the 3.0T were greater than those of the 1.5T, and these errors were not of an acceptable level. The x coordinate error was the smallest and the z coordinate error was the greatest regardless of the MRI sequence. The T2 sequence was the most accurate sequence.
Keywords: Functional neurosurgery; MRI; Stereotactic radiosurgery.
Figures


References
-
- Bradford R, Thomas DG, Bydder GM. MRI-directed stereotactic biopsy of cerebral lesions. Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wien) 1987;39:25–27. - PubMed
-
- Choi DR, Ahn YC, Kim DY, Huh SJ, Lee JI. Accuracy in target localization in stereotactic radiosurgery. Med Dosim. 1997;22:53–58. - PubMed
-
- Dammann P, Kraff O, Wrede KH, Özkan N, Orzada S, Mueller OM, et al. Evaluation of hardware-related geometrical distortion in structural MRI at 7 Tesla for image-guided applications in neurosurgery. Acad Radiol. 2011;18:910–916. - PubMed
-
- Fransson A, Andreo P, Pötter R. Aspects of MR image distortions in radiotherapy treatment planning. Strahlenther Onkol. 2001;177:59–73. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

