Chemokine CXCL1 enhances inflammatory pain and increases NMDA receptor activity and COX-2 expression in spinal cord neurons via activation of CXCR2
- PMID: 24852102
- PMCID: PMC4194227
- DOI: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2014.05.014
Chemokine CXCL1 enhances inflammatory pain and increases NMDA receptor activity and COX-2 expression in spinal cord neurons via activation of CXCR2
Abstract
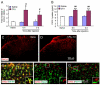
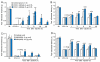
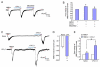
Recent studies have shown that CXCL1 upregulation in spinal astrocytes is involved in the maintenance of neuropathic pain. However, whether and how CXCL1 regulates inflammatory pain remains unknown. Here we show that intraplantar injection of CFA increased mRNA and protein expressions of CXCL1 and its major receptor CXCR2 in the spinal cord at 6h and 3days after the injection. Immunofluorescence double staining showed that CXCL1 and CXCR2 were expressed in spinal astrocytes and neurons, respectively. Intrathecal injection of CXCL1 neutralizing antibody or CXCR2 antagonist SB225002 attenuated CFA-induced mechanical and heat hypersensitivity on post-CFA day 3. Patch-clamp recordings showed that CXCL1 potentiated NMDA-induced currents in lamina II neurons via CXCR2, and this potentiation was further increased in CFA-treated mice. Furthermore, intrathecal injection of CXCL1 increased COX-2 expression in dorsal horn neurons, which was blocked by pretreatment with SB225002 or MEK (ERK kinase) inhibitor PD98059. Finally, pretreatment with SB225002 or PD98059 decreased CFA-induced heat hyperalgesia and COX-2 mRNA/protein expression and ERK activation in the spinal cord. Taken together, our data suggest that CXCL1, upregulated and released by spinal astrocytes after inflammation, acts on CXCR2-expressing spinal neurons to increase ERK activation, synaptic transmission and COX-2 expression in dorsal horn neurons and contributes to the pathogenesis of inflammatory pain.
Keywords: Astrocytes; Astroglial–neuronal interaction; COX-2; CXCL1; CXCR2; Chemokines; Complete Freund's adjuvant; ERK; Inflammatory pain.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Chemokine contribution to neuropathic pain: respective induction of CXCL1 and CXCR2 in spinal cord astrocytes and neurons.Pain. 2013 Oct;154(10):2185-2197. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2013.07.002. Epub 2013 Jul 4. Pain. 2013. PMID: 23831863 Free PMC article.
-
Chemokine receptor CXCR2 in dorsal root ganglion contributes to the maintenance of inflammatory pain.Brain Res Bull. 2016 Oct;127:219-225. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2016.09.016. Epub 2016 Sep 30. Brain Res Bull. 2016. PMID: 27697507
-
NFκB-mediated CXCL1 production in spinal cord astrocytes contributes to the maintenance of bone cancer pain in mice.J Neuroinflammation. 2014 Mar 1;11:38. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-11-38. J Neuroinflammation. 2014. PMID: 24580964 Free PMC article.
-
The role of CXCL1/CXCR2 axis in neurological diseases.Int Immunopharmacol. 2023 Jul;120:110330. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110330. Epub 2023 May 27. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37247498 Review.
-
Chemokines in neuron-glial cell interaction and pathogenesis of neuropathic pain.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017 Sep;74(18):3275-3291. doi: 10.1007/s00018-017-2513-1. Epub 2017 Apr 7. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 28389721 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Crosstalk between NFκB-dependent astrocytic CXCL1 and neuron CXCR2 plays a role in descending pain facilitation.J Neuroinflammation. 2019 Jan 3;16(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1391-2. J Neuroinflammation. 2019. PMID: 30606213 Free PMC article.
-
Conditions Mimicking the Cancer Microenvironment Modulate the Functional Outcome of Human Chorionic Villus Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells in vitro.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jun 21;9:650125. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.650125. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34235143 Free PMC article.
-
Modifying tetramethyl-nitrophenyl-imidazoline with amino acids: design, synthesis, and 3D-QSAR for improving inflammatory pain therapy.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Apr 22;9:2329-42. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S76218. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 25960636 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil-Derived COX-2 has a Key Role during Inflammatory Hyperalgesia.Inflammation. 2022 Dec;45(6):2280-2293. doi: 10.1007/s10753-022-01690-5. Epub 2022 Jul 15. Inflammation. 2022. PMID: 35840810
-
Neuraxial Cytokines in Pain States.Front Immunol. 2020 Jan 28;10:3061. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.03061. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32047493 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baba H, Ji RR, Kohno T, Moore KA, Ataka T, Wakai A, Okamoto M, Woolf CJ. Removal of GABAergic inhibition facilitates polysynaptic A fiber-mediated excitatory transmission to the superficial spinal dorsal horn. Molecular and cellular neurosciences. 2003;24:818–830. - PubMed
-
- Cartier L, Hartley O, Dubois-Dauphin M, Krause KH. Chemokine receptors in the central nervous system: role in brain inflammation and neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2005;48:16–42. - PubMed
-
- Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, Chung JM, Yaksh TL. Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. Journal of neuroscience methods. 1994;53:55–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

