Vortioxetine restores reversal learning impaired by 5-HT depletion or chronic intermittent cold stress in rats
- PMID: 24852131
- PMCID: PMC4162520
- DOI: 10.1017/S1461145714000571
Vortioxetine restores reversal learning impaired by 5-HT depletion or chronic intermittent cold stress in rats
Abstract
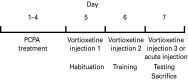
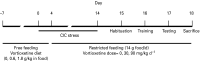
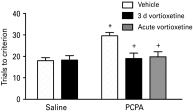
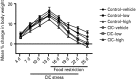
Current treatments for depression, including serotonin-specific reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), are only partially effective, with a high incidence of residual symptoms, relapse, and treatment resistance. Loss of cognitive flexibility, a component of depression, is associated with dysregulation of the prefrontal cortex. Reversal learning, a form of cognitive flexibility, is impaired by chronic stress, a risk factor for depression, and the stress-induced impairment in reversal learning is sensitive to chronic SSRI treatment, and is mimicked by serotonin (5-HT) depletion. Vortioxetine, a novel, multimodal-acting antidepressant, is a 5-HT3, 5-HT7 and 5-HT1D receptor antagonist, a 5-HT1B receptor partial agonist, a 5-HT1A receptor agonist, and inhibits the 5-HT transporter. Using adult male rats, we first investigated the direct effects of vortioxetine, acting at post-synaptic 5-HT receptors, on reversal learning that was compromised by 5-HT depletion using 4-chloro-DL-phenylalanine methyl ester hydrochloride (PCPA), effectively eliminating any contribution of 5-HT reuptake blockade. PCPA induced a reversal learning impairment that was alleviated by acute or sub-chronic vortioxetine administration, suggesting that post-synaptic 5-HT receptor activation contributes to the effects of vortioxetine. We then investigated the effects of chronic dietary administration of vortioxetine on reversal learning that had been compromised in intact animals exposed to chronic intermittent cold (CIC) stress, to assess vortioxetine's total pharmacological effect. CIC stress impaired reversal learning, and chronic vortioxetine administration prevented the reversal-learning deficit. Together, these results suggest that the direct effect of vortioxetine at 5-HT receptors may contribute to positive effects on cognitive flexibility deficits, and may enhance the effect of 5-HT reuptake blockade.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Vortioxetine, but not escitalopram or duloxetine, reverses memory impairment induced by central 5-HT depletion in rats: evidence for direct 5-HT receptor modulation.Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014 Jan;24(1):148-59. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2013.10.011. Epub 2013 Nov 4. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24284262
-
Vortioxetine dose-dependently reverses 5-HT depletion-induced deficits in spatial working and object recognition memory: a potential role for 5-HT1A receptor agonism and 5-HT3 receptor antagonism.Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014 Jan;24(1):160-71. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2013.07.001. Epub 2013 Aug 2. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 23916504
-
Chronic Vortioxetine Treatment Reduces Exaggerated Expression of Conditioned Fear Memory and Restores Active Coping Behavior in Chronically Stressed Rats.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017 Apr 1;20(4):316-323. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyw105. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27927740 Free PMC article.
-
Vortioxetine, a novel antidepressant with multimodal activity: review of preclinical and clinical data.Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Jan;145:43-57. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2014.07.001. Epub 2014 Jul 9. Pharmacol Ther. 2015. PMID: 25016186 Review.
-
[Pharmacological properties of vortioxetine and its pre-clinical consequences].Encephale. 2016 Feb;42(1 Suppl 1):1S12-23. doi: 10.1016/S0013-7006(16)30015-X. Encephale. 2016. PMID: 26879252 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Acute psilocybin enhances cognitive flexibility in rats.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jan 9:2023.01.09.523291. doi: 10.1101/2023.01.09.523291. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Neuropsychopharmacology. 2023 Jun;48(7):1011-1020. doi: 10.1038/s41386-023-01545-z. PMID: 36712091 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
A Network Meta-Analysis Comparing Effects of Various Antidepressant Classes on the Digit Symbol Substitution Test (DSST) as a Measure of Cognitive Dysfunction in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018 Feb 1;21(2):97-107. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyx070. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29053849 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Astroglial Serotonin Receptors as the Central Target of Classic Antidepressants.Adv Neurobiol. 2021;26:317-347. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-77375-5_13. Adv Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 34888840 Free PMC article.
-
Vortioxetine Reverses Impairment of Visuospatial Memory and Cognitive Flexibility Induced by Degarelix as a Model of Androgen Deprivation Therapy in Rats.Neuroendocrinology. 2024;114(3):279-290. doi: 10.1159/000535365. Epub 2023 Dec 16. Neuroendocrinology. 2024. PMID: 38104552 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological evidence that 5-HT2C receptor blockade selectively improves decision making when rewards are paired with audiovisual cues in a rat gambling task.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017 Oct;234(20):3091-3104. doi: 10.1007/s00213-017-4696-4. Epub 2017 Jul 21. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017. PMID: 28733811
References
-
- Amat J, Baratta MV, Paul E, Bland ST, Watkins LR, Maier SF (2005) Medial prefrontal cortex determines how stressor controllability affects behavior and dorsal raphe nucleus. Nature Neurosci 8:365–371 - PubMed
-
- Areberg J, Luntang-Jensen M, Sogaard B, Nilausen DO (2012) Occupancy of the serotonin transporter after administration of Lu AA21004 and its relation to plasma concentration in healthy subjects. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 110:401–404 - PubMed
-
- Artigas F, Celada P, Laruelle M, Adell A (2001) How does pindolol improve antidepressant action? Trends Pharmacol Sci 22:224–228 - PubMed
-
- Austin M-P, Mitchell P, Goodwin GM (2001) Cognitive deficits in depression: possible implications for functional neuropathology. Brit J Psychiatry 178:200–206 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

