RNA-Seq and expression microarray highlight different aspects of the fetal amniotic fluid transcriptome
- PMID: 24852236
- PMCID: PMC4184931
- DOI: 10.1002/pd.4417
RNA-Seq and expression microarray highlight different aspects of the fetal amniotic fluid transcriptome
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to compare the complexity of the amniotic fluid supernatant cell-free fetal transcriptome as described by RNA Sequencing (RNA-Seq) and gene expression microarrays.
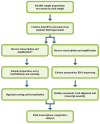
Methods: Cell-free fetal RNA from the amniotic fluid supernatant of five euploid mid-trimester samples was divided and prepared in tandem for analysis by either the Affymetrix HG-U133 Plus 2.0 Gene Chip microarray or Illumina HiSeq. Transcriptomes were assembled and compared on the basis of the presence of signal, rank-order gene expression, and pathway enrichment using Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA). RNA-Seq data were also examined for evidence of alternative splicing.
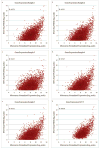
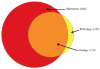
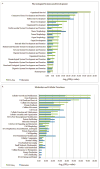
Results: Within individual samples, gene expression was strongly correlated (R = 0.43-0.57). Fewer expressed genes were observed using RNA-Seq than gene expression microarrays (4158 vs 8842). Most of the top pathways in the 'Physiological Systems Development and Function' IPA category were shared between platforms, although RNA-Seq yielded more significant p-values. Using RNA-Seq, examples of known alternative splicing were detected in several genes including H19 and IGF2.
Conclusions: In this pilot study, we found that expression microarrays gave a broader view of overall gene expression, while RNA-Seq demonstrated alternative splicing and specific pathways relevant to the developing fetus. The degraded nature of cell-free fetal RNA presented technical challenges for the RNA-Seq approach.
© 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Amniotic Fluid Cell-Free Transcriptome Provides Novel Information about Fetal Development and Placental Cellular Dynamics.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 5;22(5):2612. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052612. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33807645 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Global gene expression changes of amniotic fluid cell free RNA according to fetal development.Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2017 Sep;216:104-110. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2017.07.017. Epub 2017 Jul 15. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2017. PMID: 28750298
-
The amniotic fluid transcriptome: a source of novel information about human fetal development.Obstet Gynecol. 2012 Jan;119(1):111-8. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0b013e31823d4150. Obstet Gynecol. 2012. PMID: 22183218 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the cell-free amniotic fluid transcriptome expressed during the euploid mid-trimester of pregnancy.Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2016 Aug;203:94-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2016.05.040. Epub 2016 May 27. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2016. PMID: 27261819
-
Comparing bioinformatic gene expression profiling methods: microarray and RNA-Seq.Med Sci Monit Basic Res. 2014 Aug 23;20:138-42. doi: 10.12659/MSMBR.892101. Med Sci Monit Basic Res. 2014. PMID: 25149683 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The amniotic fluid transcriptome as a guide to understanding fetal disease.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2015 Feb 13;5(4):a023101. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a023101. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2015. PMID: 25680981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Utility of Circulating Cell-Free RNA Analysis for the Characterization of Global Transcriptome Profiles of Multiple Myeloma Patients.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Jun 25;11(6):887. doi: 10.3390/cancers11060887. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31242667 Free PMC article.
-
The Amniotic Fluid Cell-Free Transcriptome Provides Novel Information about Fetal Development and Placental Cellular Dynamics.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 5;22(5):2612. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052612. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33807645 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted expression profiling by RNA-Seq improves detection of cellular dynamics during pregnancy and identifies a role for T cells in term parturition.Sci Rep. 2019 Jan 29;9(1):848. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-36649-w. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30696862 Free PMC article.
-
Amniotic fluid transcriptomics reflects novel disease mechanisms in fetuses with myelomeningocele.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2017 Nov;217(5):587.e1-587.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2017.07.022. Epub 2017 Jul 20. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2017. PMID: 28735706 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Larrabee PB, Johnson KL, Lai C, et al. Global gene expression analysis in the living human fetus using amniotic fluid: a feasibility study. JAMA. 2005;293:836–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous