Context-dependent signal integration by the GLI code: the oncogenic load, pathways, modifiers and implications for cancer therapy
- PMID: 24852887
- PMCID: PMC4151135
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.05.003
Context-dependent signal integration by the GLI code: the oncogenic load, pathways, modifiers and implications for cancer therapy
Abstract
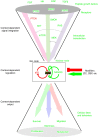
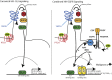
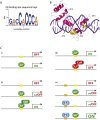
Canonical Hedgehog (HH) signaling leads to the regulation of the GLI code: the sum of all positive and negative functions of all GLI proteins. In humans, the three GLI factors encode context-dependent activities with GLI1 being mostly an activator and GLI3 often a repressor. Modulation of GLI activity occurs at multiple levels, including by co-factors and by direct modification of GLI structure. Surprisingly, the GLI proteins, and thus the GLI code, is also regulated by multiple inputs beyond HH signaling. In normal development and homeostasis these include a multitude of signaling pathways that regulate proto-oncogenes, which boost positive GLI function, as well as tumor suppressors, which restrict positive GLI activity. In cancer, the acquisition of oncogenic mutations and the loss of tumor suppressors - the oncogenic load - regulates the GLI code toward progressively more activating states. The fine and reversible balance of GLI activating GLI(A) and GLI repressing GLI(R) states is lost in cancer. Here, the acquisition of GLI(A) levels above a given threshold is predicted to lead to advanced malignant stages. In this review we highlight the concepts of the GLI code, the oncogenic load, the context-dependency of GLI action, and different modes of signaling integration such as that of HH and EGF. Targeting the GLI code directly or indirectly promises therapeutic benefits beyond the direct blockade of individual pathways.
Keywords: Cancer; Development; GLI transcription factors; Hedgehog-GLI signaling; Oncogenes; Signal transduction; Signaling integration; Stem cells.
Copyright © 2014 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Tabata T., Eaton S., Kornberg T.B. The Drosophila hedgehog gene is expressed specifically in posterior compartment cells and is a target of engrailed regulation. Genes Dev. 1992;6:2635–2645. - PubMed
-
- Forbes A.J., Nakano Y., Taylor A.M., Ingham P.W. Genetic analysis of hedgehog signalling in the Drosophila embryo. Development. 1993;11:2–5. 4. - PubMed
-
- Nakano Y., Guerrero I., Hidalgo A., Taylor A., Whittle J.R., Ingham P.W. A protein with several possible membrane-spanning domains encoded by the Drosophila segment polarity gene patched. Nature. 1989;341:508–513. - PubMed
-
- Lee J.J., von Kessler D.P., Parks S., Beachy P.A. Secretion and localized transcription suggest a role in positional signaling for products of the segmentation gene hedgehog. Cell. 1992;71:33–50. - PubMed
-
- Mohler J., Vani K. Molecular organization and embryonic expression of the hedgehog gene involved in cell-cell communication in segmental patterning of Drosophila. Development. 1992;115:957–971. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

