Mangiferin facilitates islet regeneration and β-cell proliferation through upregulation of cell cycle and β-cell regeneration regulators
- PMID: 24853132
- PMCID: PMC4057772
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms15059016
Mangiferin facilitates islet regeneration and β-cell proliferation through upregulation of cell cycle and β-cell regeneration regulators
Abstract
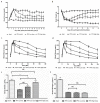
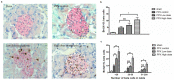
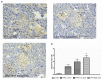
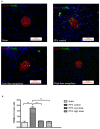
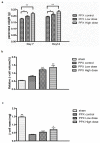
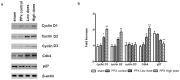
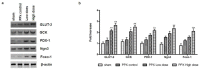
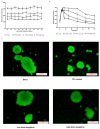
Mangiferin, a xanthonoid found in plants including mangoes and iris unguicularis, was suggested in previous studies to have anti-hyperglycemic function, though the underlying mechanisms are largely unknown. This study was designed to determine the therapeutic effect of mangiferin by the regeneration of β-cells in mice following 70% partial pancreatectomy (PPx), and to explore the mechanisms of mangiferin-induced β-cell proliferation. For this purpose, adult C57BL/6J mice after 7-14 days post-PPx, or a sham operation were subjected to mangiferin (30 and 90 mg/kg body weight) or control solvent injection. Mangiferin-treated mice exhibited an improved glycemia and glucose tolerance, increased serum insulin levels, enhanced β-cell hyperplasia, elevated β-cell proliferation and reduced β-cell apoptosis. Further dissection at the molecular level showed several key regulators of cell cycle, such as cyclin D1, D2 and cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (Cdk4) were significantly up-regulated in mangiferin-treated mice. In addition, critical genes related to β-cell regeneration, such as pancreatic and duodenal homeobox 1 (PDX-1), neurogenin 3 (Ngn3), glucose transporter 2 (GLUT-2), Forkhead box protein O1 (Foxo-1), and glucokinase (GCK), were found to be promoted by mangiferin at both the mRNA and protein expression level. Thus, mangiferin administration markedly facilitates β-cell proliferation and islet regeneration, likely by regulating essential genes in the cell cycle and the process of islet regeneration. These effects therefore suggest that mangiferin bears a therapeutic potential in preventing and/or treating the diabetes.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mangiferin induces islet regeneration in aged mice through regulating p16INK4a.Int J Mol Med. 2018 Jun;41(6):3231-3242. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3524. Epub 2018 Mar 1. Int J Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29512742 Free PMC article.
-
Agaricus bisporus lectins mediates islet β-cell proliferation through regulation of cell cycle proteins.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2012 Mar;237(3):287-96. doi: 10.1258/ebm.2011.011251. Epub 2012 Mar 5. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2012. PMID: 22393165
-
Antihyperglycemic effect of ginsenoside Rh2 by inducing islet β-cell regeneration in mice.Horm Metab Res. 2012 Jan;44(1):33-40. doi: 10.1055/s-0031-1295416. Epub 2011 Dec 28. Horm Metab Res. 2012. PMID: 22205570
-
Newer perspective on the coupling between glucose-mediated signaling and β-cell functionality.Endocr J. 2020 Jan 28;67(1):1-8. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ19-0335. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Endocr J. 2020. PMID: 31694991 Review.
-
Mangiferin and Cancer: Mechanisms of Action.Nutrients. 2016 Jun 28;8(7):396. doi: 10.3390/nu8070396. Nutrients. 2016. PMID: 27367721 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of the Antidiabetic Potential of Xanthone-Rich Extracts from Gentiana dinarica and Gentiana utriculosa.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 21;25(16):9066. doi: 10.3390/ijms25169066. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201752 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential of South African Herbal Tisanes, Rooibos and Honeybush in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Molecules. 2018 Dec 5;23(12):3207. doi: 10.3390/molecules23123207. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30563087 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Edible Plant-Derived Xanthones as Functional Food Components for Metabolic Syndrome Mitigation: Bioactivities and Mechanisms.Foods. 2025 Jul 1;14(13):2344. doi: 10.3390/foods14132344. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40647096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mango leaf extract improves central pathology and cognitive impairment in a type 2 diabetes mouse model.Brain Pathol. 2017 Jul;27(4):499-507. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12433. Epub 2016 Nov 24. Brain Pathol. 2017. PMID: 27537110 Free PMC article.
-
The therapeutic potential of natural products for treating pancreatic cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Nov 2;13:1051952. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1051952. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36408249 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dean P.G., Kudva Y.C., Stegall M.D. Long-term benefits of pancreas transplantation. Curr. Opin. Organ Tranplant. 2008;13:85–90. - PubMed
-
- Shapiro A.J., Ricordi C., Hering B.J., Auchincloss H., Lindblad R., Robertson R.P., Secchi A., Brendel M.D., Berney T., Brennan D.C. International trial of the Edmonton protocol for islet transplantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006;355:1318–1330. - PubMed
-
- Bonner-Weir S., Sharma A. Are there pancreatic progenitor cells from which new islets form after birth? Nat. Clin. Pract. 2006;2:240–224. - PubMed
-
- Palmer J.P., McCulloch D.K. Prediction and prevention of IDDM—1991. Diabetes. 1991;40:943–947. - PubMed
-
- Mauricio D., Mandrup-Poulsen T. Apoptosis and the pathogenesis of IDDM: A question of life and death. Diabetes. 1998;47:1537–1543. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

