Improving intra-fractional target position accuracy using a 3D surface surrogate for left breast irradiation using the respiratory-gated deep-inspiration breath-hold technique
- PMID: 24853144
- PMCID: PMC4031138
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097933
Improving intra-fractional target position accuracy using a 3D surface surrogate for left breast irradiation using the respiratory-gated deep-inspiration breath-hold technique
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the use of 3D optical surface imaging as a surrogate for respiratory gated deep-inspiration breath-hold (DIBH) for left breast irradiation.
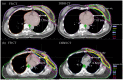
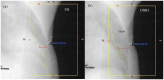
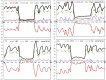
Material and methods: Patients with left-sided breast cancer treated with lumpectomy or mastectomy were selected as candidates for DIBH treatment for their external beam radiation therapy. Treatment plans were created on both free breathing (FB) and DIBH computed tomography (CT) simulation scans to determine dosimetric benefits from DIBH. The Real-time Position Management (RPM) system was used to acquire patient's breathing trace during DIBH CT acquisition and treatment delivery. The reference 3D surface models from FB and DIBH CT scans were generated and transferred to the "AlignRT" system for patient positioning and real-time treatment monitoring. MV Cine images were acquired during treatment for each beam as quality assurance for intra-fractional position verification. The chest wall excursions measured on these images were used to define the actual target position during treatment, and to investigate the accuracy and reproducibility of RPM and AlignRT.
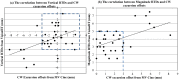
Results: Reduction in heart dose can be achieved using DIBH for left breast/chest wall radiation. RPM was shown to have inferior correlation with the actual target position, as determined by the MV Cine imaging. Therefore, RPM alone may not be an adequate surrogate in defining the breath-hold level. Alternatively, the AlignRT surface imaging demonstrated a superior correlation with the actual target positioning during DIBH. Both the vertical and magnitude real-time deltas (RTDs) reported by AlignRT can be used as the gating parameter, with a recommended threshold of ±3 mm and 5 mm, respectively.
Conclusion: The RPM system alone may not be sufficient for the required level of accuracy in left-sided breast/CW DIBH treatments. The 3D surface imaging can be used to ensure patient setup and monitor inter- and intra- fractional motions. Furthermore, the target position accuracy during DIBH treatment can be improved by AlignRT as a superior surrogate, in addition to the RPM system.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






References
-
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists' Collaborative Group (EBCTCG) (2011) Darby S, McGale P, Correa C, Taylor C, et al. (2011) Effect of radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery on 10-year recurrence and 15-year breast cancer death: Meta-analysis of individual patient data for 10,801 women in 17 randomised trials. Lancet 378: 1707–1716. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fisher B, Anderson S, Bryant J, Margolese RG, Deutsch M, et al. (2002) Twenty-year follow-up of a randomized trial comparing total mastectomy, lumpectomy, and lumpectomy plus irradiation for the treatment of invasive breast cancer. N Engl J Med 347: 1233–1241. - PubMed
-
- Clarke M, Collins R, Darby S, Davies C, Elphinstone P, et al. (2005) Effects of radiotherapy and of differences in the extent of surgery for early breast cancer on local recurrence and 15-year survival: An overview of the randomised trials. Lancet 366: 2087–2106. - PubMed
-
- Bouillon K, Haddy N, Delaloge S, Garbay JR, Garsi JP, et al. (2011) Long-term cardiovascular mortality after radiotherapy for breast cancer. J Am Coll Cardiol 57: 445–452. - PubMed
-
- McGale P, Darby SC, Hall P, Adolfsson J, Bengtsson NO, et al. (2011) Incidence of heart disease in 35,000 women treated with radiotherapy for breast cancer in denmark and sweden. Radiother Oncol 100: 167–175. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

