Knockout of endothelial cell-derived endothelin-1 attenuates skin fibrosis but accelerates cutaneous wound healing
- PMID: 24853267
- PMCID: PMC4031171
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097972
Knockout of endothelial cell-derived endothelin-1 attenuates skin fibrosis but accelerates cutaneous wound healing
Abstract
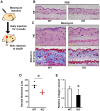
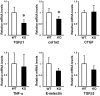
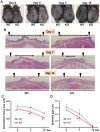
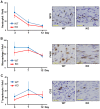
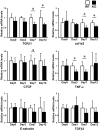
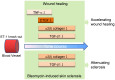
Endothelin (ET)-1 is known for the most potent vasoconstrictive peptide that is released mainly from endothelial cells. Several studies have reported ET-1 signaling is involved in the process of wound healing or fibrosis as well as vasodilation. However, little is known about the role of ET-1 in these processes. To clarify its mechanism, we compared skin fibrogenesis and wound repair between vascular endothelial cell-specific ET-1 knockout mice and their wild-type littermates. Bleomycin-injected fibrotic skin of the knockout mice showed significantly decreased skin thickness and collagen content compared to that of wild-type mice, indicating that bleomycin-induced skin fibrosis is attenuated in the knockout mice. The mRNA levels of transforming growth factor (TGF)-β were decreased in the bleomycin-treated skin of ET-1 knockout mice. On the other hand, skin wound healing was accelerated in ET-1 knockout mice, which was indicated by earlier granulation tissue reduction and re-epithelialization in these mice. The mRNA levels of TGF-β, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) were reduced in the wound of ET-1 knockout mice. In endothelial ET-1 knockout mouse, the expression of TNF-α, CTGF and TGF-β was down-regulated. Bosentan, an antagonist of dual ET receptors, is known to attenuate skin fibrosis and accelerate wound healing in systemic sclerosis, and such contradictory effect may be mediated by above molecules. The endothelial cell-derived ET-1 is the potent therapeutic target in fibrosis or wound healing, and investigations of the overall regulatory mechanisms of these pathological conditions by ET-1 may lead to a new therapeutic approach.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Endothelin 1 contributes to the effect of transforming growth factor beta1 on wound repair and skin fibrosis.Arthritis Rheum. 2010 Mar;62(3):878-89. doi: 10.1002/art.27307. Arthritis Rheum. 2010. PMID: 20131241
-
[Effect of hydrocinnamoyl-L-valyl pyrrolidine on healing quality of deep partial-thickness scald wound in mice].Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2016 Nov 20;32(11):658-666. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-2587.2016.11.005. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27894387 Chinese.
-
GSK-3beta in mouse fibroblasts controls wound healing and fibrosis through an endothelin-1-dependent mechanism.J Clin Invest. 2008 Oct;118(10):3279-90. doi: 10.1172/JCI35381. J Clin Invest. 2008. Retraction in: J Clin Invest. 2008 Nov;118(11):3812. doi: 10.1172/jci35381r1. PMID: 18802478 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Growth regulation of skin fibroblasts.J Dermatol Sci. 2000 Dec;24 Suppl 1:S70-7. doi: 10.1016/s0923-1811(00)00144-4. J Dermatol Sci. 2000. PMID: 11137399 Review.
-
Targeting the TGFbeta, endothelin-1 and CCN2 axis to combat fibrosis in scleroderma.Cell Signal. 2008 Aug;20(8):1409-14. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2008.01.006. Epub 2008 Jan 19. Cell Signal. 2008. PMID: 18296024 Review.
Cited by
-
Autocrine and Paracrine Effects of Vascular Endothelial Cells Promote Cutaneous Wound Healing.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Apr 10;2021:6695663. doi: 10.1155/2021/6695663. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 33937411 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Endothelin-1 in Aqueous Humor on Intermediate-Term Trabeculectomy Outcomes.J Ophthalmol. 2016;2016:2401976. doi: 10.1155/2016/2401976. Epub 2016 Jan 21. J Ophthalmol. 2016. PMID: 26904271 Free PMC article.
-
Spinal cord vascular degeneration impairs duloxetine penetration.Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2023 May 26;4:1190440. doi: 10.3389/fpain.2023.1190440. eCollection 2023. Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37325676 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-specific expression of the transcriptional regulator RHAMM provides a timing mechanism that controls appropriate wound re-epithelialization.J Biol Chem. 2020 Apr 17;295(16):5427-5448. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.010002. Epub 2020 Mar 12. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32165498 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal miR-767 from senescent endothelial-derived accelerating skin fibroblasts aging via inhibiting TAB1.J Mol Histol. 2023 Feb;54(1):13-24. doi: 10.1007/s10735-022-10107-4. Epub 2022 Nov 21. J Mol Histol. 2023. PMID: 36409439 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barton M, Yanagisawa M (2008) Endothelin: 20 years from discovery to therapy. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 86: 485–498. - PubMed
-
- Sauter G, Wolf S, Risler T, Brehm B (2004) Influence of endothelin receptor antagonism on smooth muscle cell proliferation after chronic renal failure. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 44 Suppl 1S165–167. - PubMed
-
- Komuro I, Kurihara H, Sugiyama T, Yoshizumi M, Takaku F, et al. (1988) Endothelin stimulates c-fos and c-myc expression and proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells. FEBS Lett 238: 249–252. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

