Rasfonin, a novel 2-pyrone derivative, induces ras-mutated Panc-1 pancreatic tumor cell death in nude mice
- PMID: 24853419
- PMCID: PMC4047882
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2014.213
Rasfonin, a novel 2-pyrone derivative, induces ras-mutated Panc-1 pancreatic tumor cell death in nude mice
Abstract
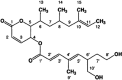
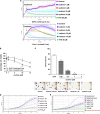
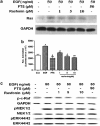
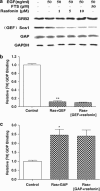
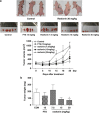
Rasfonin is a novel 2-pyrone derivative reported to induce apoptosis in ras-dependent cells. In this study, its effects on ras-mutated pancreatic cancer cells were investigated in vitro and in vivo. Two human pancreatic cancer cell lines Panc-1 (mutated K-ras) and BxPC-3 (wild-type K-ras) were selected to test the effects of rasfonin on cell proliferation, clone formation, migration and invasion in vitro. Immunoblotting was used to detect the expressions of EGFR-Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK signaling pathway proteins. Ras activity was measured using a pull-down ELISA kit and guanine exchange factor (GEF)/GTPase-activating proteins (GAP) activity was measured by [(3)H]-GDP radiometric ligand binding. For an in vivo study, CD1 nude mice bearing Panc-1 cells were treated with rasfonin or Salirasib (FTS). We found that rasfonin suppressed proliferation more strongly in Panc-1 cells (IC50=5.5 μM) than BxPC-3 cells (IC50=10 μM) in vitro. Clone formation, migration and invasion by Panc-1 cells were also reduced by rasfonin. Rasfonin had little effect on the farnesylation of Ras, but it strongly downregulated Ras activity and consequently phosphorylation of c-Raf/MEK/ERK. Further experiments indicated that rasfonin reduced Son of sevenless (Sos1) expression but did not alter GEF and GAP activities. The in vivo experiments also revealed that rasfonin (30 mg/kg) delayed the growth of xenograft tumors originating from Panc-1 cells. Tumor weight was ultimately decreased after 20 days of treatment of rasfonin. Rasfonin is a robust inhibitor of pancreatic cancers with the K-ras mutation. The reduction of Sos1 expression and the consequently depressed Ras-MAPK activity could be important in its anticancer activity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
K-RAS mutant pancreatic tumors show higher sensitivity to MEK than to PI3K inhibition in vivo.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e44146. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044146. Epub 2012 Aug 31. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22952903 Free PMC article.
-
Dihydrosanguinarine suppresses pancreatic cancer cells via regulation of mut-p53/WT-p53 and the Ras/Raf/Mek/Erk pathway.Phytomedicine. 2019 Jun;59:152895. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2019.152895. Epub 2019 Mar 16. Phytomedicine. 2019. PMID: 30913453
-
RAS nucleotide cycling underlies the SHP2 phosphatase dependence of mutant BRAF-, NF1- and RAS-driven cancers.Nat Cell Biol. 2018 Sep;20(9):1064-1073. doi: 10.1038/s41556-018-0169-1. Epub 2018 Aug 13. Nat Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 30104724 Free PMC article.
-
[Roles of targeting Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathways in the treatment of esophageal carcinoma].Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2013 May;48(5):635-41. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2013. PMID: 23888683 Review. Chinese.
-
Inhibition of the RAF/MEK/ERK Signaling Cascade in Pancreatic Cancer: Recent Advances and Future Perspectives.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 28;25(3):1631. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031631. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338909 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Baeyer-Villiger oxidation: a promising tool for the synthesis of natural products: a review.RSC Adv. 2024 Jul 25;14(32):23423-23458. doi: 10.1039/d4ra03914a. eCollection 2024 Jul 19. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39055269 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteasome inhibition attenuates rasfonin-induced autophagy concurring with the upregulation of caspase-dependent apoptosis.Mycology. 2016 Feb 26;7(1):29-35. doi: 10.1080/21501203.2016.1147091. eCollection 2016. Mycology. 2016. PMID: 30123613 Free PMC article.
-
[Rasfonin inhibits proliferation and migration of osteosarcoma 143B cells].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2019 Apr 18;51(2):234-238. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2019.02.006. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2019. PMID: 30996359 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Disruption of the pro-oncogenic c-RAF-PDE8A complex represents a differentiated approach to treating KRAS-c-RAF dependent PDAC.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 18;14(1):8998. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-59451-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38637546 Free PMC article.
-
Genome analysis of Cephalotrichum gorgonifer and identification of the biosynthetic pathway for rasfonin, an inhibitor of KRAS dependent cancer.Fungal Biol Biotechnol. 2023 Jun 24;10(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s40694-023-00158-x. Fungal Biol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37355668 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bustinza-Linares E, Kurzrock R, Tsimberidou AM. Salirasib in the treatment of pancreatic cancer. Future Oncol. 2010;6:885–891. - PubMed
-
- Abbruzzese JL. New applications of gemcitabine and future directions in the management of pancreatic cancer. Cancer. 2002;95:941–945. - PubMed
-
- Yip-Schneider MT, Sweeney CJ, Jung SH, Crowell PL, Marshall MS. Cell cycle effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and enhanced growth inhibition in combination with gemcitabine in pancreatic carcinoma cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001;298:976–985. - PubMed
-
- Hezel AF, Kimmelman AC, Stanger BZ, Bardeesy N, Depinho RA. Genetics and biology of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Genes Dev. 2006;20:1218–1249. - PubMed
-
- Talar-Wojnarowska R, Malecka-Panas E. Molecular pathogenesis of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: potential clinical implications. Med Sci Monit. 2006;12:RA186–RA193. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

