Immunoglobulin G expression in lung cancer and its effects on metastasis
- PMID: 24853685
- PMCID: PMC4031068
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097359
Immunoglobulin G expression in lung cancer and its effects on metastasis
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Immunoglobulin G Expression in Lung Cancer and Its Effects on Metastasis.PLoS One. 2020 Jan 24;15(1):e0228444. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228444. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 31978182 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
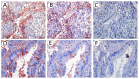
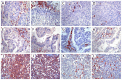
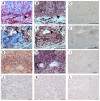
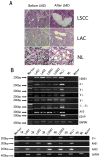
Lung cancer is one of the leading malignancies worldwide, but the regulatory mechanism of its growth and metastasis is still poorly understood. We investigated the possible expression of immunoglobulin G (IgG) genes in squamous cell carcinomas and adenocarcinomas of the lung and related cancer cell lines. Abundant mRNA of IgG and essential enzymes for IgG synthesis, recombination activation genes 1, 2 (RAG1, 2) and activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) were detected in the cancer cells but not in adjacent normal lung tissue or normal lung epithelial cell line. The extents of IgG expression in 86 lung cancers were found to associate with clinical stage, pathological grade and lymph node metastasis. We found that knockdown of IgG with siRNA resulted in decreases of cellular proliferation, migration and attachment for cultured lung cancer cells. Metastasis-associated gene 1 (MTA1) appeared to be co-expressed with IgG in lung cancer cells. Statistical analysis showed that the rate of IgG expression was significantly correlated to that of MTA1 and to lymph node metastases. Inhibition of MTA1 gene expression with siRNA also led to decreases of cellular migration and attachment for cultured lung cancer cells. These evidences suggested that inhibition of cancer migration and attachment induced by IgG down-regulation might be achieved through MTA1 regulatory pathway. Our findings suggest that lung cancer-produced IgG is likely to play an important role in cancer growth and metastasis with significant clinical implications.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



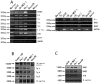

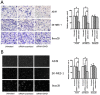

Similar articles
-
Immunoglobulin G expression in carcinomas and cancer cell lines.FASEB J. 2007 Sep;21(11):2931-8. doi: 10.1096/fj.07-8073com. Epub 2007 May 2. FASEB J. 2007. PMID: 17475920
-
MTA-1 expression is associated with metastasis and epithelial to mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer cells.Tumour Biol. 2013 Apr;34(2):1189-204. doi: 10.1007/s13277-013-0662-x. Epub 2013 Jan 31. Tumour Biol. 2013. PMID: 23371285
-
Metastasis-associated protein 1 nuclear expression is associated with tumor progression and clinical outcome in patients with non-small cell lung cancer.J Thorac Oncol. 2010 Aug;5(8):1159-66. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181e04d98. J Thorac Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20661085
-
Tumor metastasis-associated human MTA1 gene and its MTA1 protein product: role in epithelial cancer cell invasion, proliferation and nuclear regulation.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2003;20(1):19-24. doi: 10.1023/a:1022534217769. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2003. PMID: 12650603 Review.
-
The role of the MTA family and their encoded proteins in human cancers: molecular functions and clinical implications.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2009;26(3):215-27. doi: 10.1007/s10585-008-9233-8. Epub 2008 Dec 31. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2009. PMID: 19116762 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in the Outcome of Malignant Epitheliomas: Significance of CA215 Involvement.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Feb 2;14(3):328. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14030328. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38337844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of immunoglobulin A in human mesangial cells and its effects on cell apoptosis and adhesion.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Apr;17(4):5272-5282. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.8544. Epub 2018 Feb 2. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29393471 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and Clinical Significance of Non B Cell-Derived Immunoglobulins in the Urinary System and Male Reproductive System.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1445:101-117. doi: 10.1007/978-981-97-0511-5_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 38967753 Review.
-
Expression, Function, and Significance of Non B Cell-Derived Immunoglobulin in Haematological System.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1445:179-188. doi: 10.1007/978-981-97-0511-5_15. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 38967760 Review.
-
IgG silencing induces apoptosis and suppresses proliferation, migration and invasion in LNCaP prostate cancer cells.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2016 Dec 3;21:27. doi: 10.1186/s11658-016-0029-6. eCollection 2016. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2016. PMID: 28536629 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F (2011) Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, et al (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA: Cancer J Clin 61(2): 69–90. - PubMed
-
- Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O, Jemal A (2011) Cancer statistics. CA: Cancer J Clin 61(4): 212–236. - PubMed
-
- Brambilla E, Travis W, Colby T, Corrin B, Shimosato Y (2001) The new World Health Organization classification of lung tumours. Eur Respir J 18(6): 1059–1068. - PubMed
-
- Detterbeck FC, Boffa DJ, Tanoue LT (2009) The new lung cancer staging system. CHEST 136(1): 260–271. - PubMed
-
- Qiu X, Zhu X, Zhang L, Mao Y, Zhang J, et al. (2003) Human epithelial cancers secrete immunoglobulin g with unidentified specificity to promote growth and survival of tumor cells. Cancer Res 63(19): 6488–6995. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

