An extended proximal esophageal myotomy is necessary to normalize EGJ distensibility during Heller myotomy for achalasia, but not POEM
- PMID: 24853854
- PMCID: PMC4343545
- DOI: 10.1007/s00464-014-3563-1
An extended proximal esophageal myotomy is necessary to normalize EGJ distensibility during Heller myotomy for achalasia, but not POEM
Abstract
Background: For laparoscopic Heller myotomy (LHM), the optimal myotomy length proximal to the esophagogastric junction (EGJ) is unknown. In this study, we used a functional lumen imaging probe (FLIP) to measure EGJ distensibility changes resulting from variable proximal myotomy lengths during LHM and peroral esophageal myotomy (POEM).
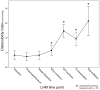
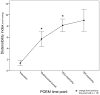
Methods: Distensibility index (DI) (defined as the minimum cross-sectional area at the EGJ divided by pressure) was measured with FLIP after each operative step. During LHM and POEM, each patient's myotomy was performed in two stages: first, a myotomy ablating only the EGJ complex was created (EGJ-M), extending from 2 cm proximal to the EGJ, to 3 cm distal to it. Next, the myotomy was lengthened 4 cm further cephalad to create an extended proximal myotomy (EP-M).
Results: Measurements were performed in 12 patients undergoing LHM and 19 undergoing POEM. LHM resulted in an overall increase in DI (1.6 ± 1 vs. 6.3 ± 3.4 mm(2)/mmHg, p < 0.001). Creation of an EGJ-M resulted in a small increase (1.6-2.3 mm(2)/mmHg, p < 0.01) and extension to an EP-M resulted in a larger increase (2.3-4.9 mm(2)/mmHg, p < 0.001). This effect was consistent, with 11 (92%) patients experiencing a larger increase after EP-M than after EGJ-M. Fundoplication resulted in a decrease in DI and deinsufflation an increase. POEM resulted in an increase in DI (1.3 ± 1 vs. 9.2 ± 3.9 mm(2)/mmHg, p < 0.001). Both creation of the submucosal tunnel and performing an EGJ-M increased DI, whereas lengthening of the myotomy to an EP-M had no additional effect. POEM resulted in a larger overall increase from baseline than LHM (7.9 ± 3.5 vs. 4.7 ± 3.3 mm(2)/mmHg, p < 0.05).
Conclusions: During LHM, an EP-M was necessary to normalize distensibility, whereas during POEM, a myotomy confined to the EGJ complex was sufficient. In this cohort, POEM resulted in a larger overall increase in EGJ distensibility.
Figures


References
-
- Triadafilopoulos G, Boeckxstaens GE, Gullo R, Patti MG, Pandolfino JE, Kahrilas PJ, Duranceau A, Jamieson G, Zaninotto G. The Kagoshima consensus on esophageal achalasia. Dis Esophagus; 2012;25:337–48. - PubMed
-
- Boeckxstaens GE, Annese V, des Varannes SB, Chaussade S, Costantini M, Cuttitta A, Elizalde JI, Fumagalli U, Gaudric M, Rohof WO, Smout AJ, Tack J, Zwinderman AH, Zaninotto G, Busch OR European Achalasia Trial I . Pneumatic dilation versus laparoscopic Heller’s myotomy for idiopathic achalasia. N Engl J Med; 2011;364:1807–16. - PubMed
-
- Yaghoobi M, Mayrand S, Martel M, Roshan-Afshar I, Bijarchi R, Barkun A. Laparoscopic Heller’s myotomy versus pneumatic dilation in the treatment of idiopathic achalasia: a meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Gastrointest Endosc; 2013;78:468–75. - PubMed
-
- Campos GM, Vittinghoff E, Rabl C, Takata M, Gadenstatter M, Lin F, Ciovica R. Endoscopic and surgical treatments for achalasia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Surg; 2009;249:45–57. - PubMed
-
- Inoue H, Minami H, Kobayashi Y, Sato Y, Kaga M, Suzuki M, Satodate H, Odaka N, Itoh H, Kudo S. Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) for esophageal achalasia. Endoscopy; 2010;42:265–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

