Diet-gene interactions and PUFA metabolism: a potential contributor to health disparities and human diseases
- PMID: 24853887
- PMCID: PMC4042578
- DOI: 10.3390/nu6051993
Diet-gene interactions and PUFA metabolism: a potential contributor to health disparities and human diseases
Abstract
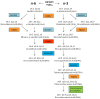
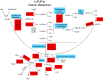
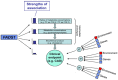
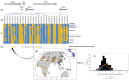
The "modern western" diet (MWD) has increased the onset and progression of chronic human diseases as qualitatively and quantitatively maladaptive dietary components give rise to obesity and destructive gene-diet interactions. There has been a three-fold increase in dietary levels of the omega-6 (n-6) 18 carbon (C18), polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) linoleic acid (LA; 18:2n-6), with the addition of cooking oils and processed foods to the MWD. Intense debate has emerged regarding the impact of this increase on human health. Recent studies have uncovered population-related genetic variation in the LCPUFA biosynthetic pathway (especially within the fatty acid desaturase gene (FADS) cluster) that is associated with levels of circulating and tissue PUFAs and several biomarkers and clinical endpoints of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Importantly, populations of African descent have higher frequencies of variants associated with elevated levels of arachidonic acid (ARA), CVD biomarkers and disease endpoints. Additionally, nutrigenomic interactions between dietary n-6 PUFAs and variants in genes that encode for enzymes that mobilize and metabolize ARA to eicosanoids have been identified. These observations raise important questions of whether gene-PUFA interactions are differentially driving the risk of cardiovascular and other diseases in diverse populations, and contributing to health disparities, especially in African American populations.
Figures
References
-
- Cordain L., Eaton S.B., Sebastian A., Mann N., Lindeberg S., Watkins B.A., O’Keefe J.H., Brand-Miller J. Origins and evolution of the Western diet: Health implications for the 21st century. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005;81:341–354. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

