Period, birth cohort and prevalence of dementia in mainland China, Hong Kong and Taiwan: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 24854229
- PMCID: PMC4552972
- DOI: 10.1002/gps.4148
Period, birth cohort and prevalence of dementia in mainland China, Hong Kong and Taiwan: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: There have been dramatic societal changes in East Asia over the last hundred years. Several of the established risk factors could have important period and cohort effects. This study explores temporal variation of dementia prevalence in mainland China, Hong Kong and Taiwan taking study methods into account.
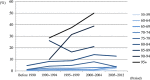
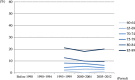
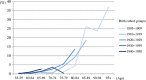
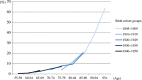
Methods: Seventy prevalence studies of dementia in mainland China, Hong Kong and Taiwan were identified from 1980 to 2012. Five period groups (before 1990, 1990 ~ 1994, 1995 ~ 1999, 2000 ~ 2004 and 2005 ~ 2012) and five birth cohort groups (1895 ~ 1909, 1910 ~ 1919, 1920 ~ 1929, 1930 ~ 1939 and 1940 ~ 1950) were categorised using the year of investigation and 5-year age groups. Pooled prevalence by age, period and birth cohort groups was estimated through meta-regression model and meta-analysis taking diagnostic criteria and age structure into account.
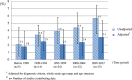
Results: After adjusting for diagnostic criteria, the study age range and age structure, the prevalence of dementia in the older population aged 60 years and over fluctuated across periods but not reaching significance and were estimated as 1.8%, 2.5%, 2.1%, 2.4% and 3.1% for the five periods from pre-1990 to 2005 ~ 2012. A potential increasing pattern from less to more recent birth cohort groups was found in the major studies using older diagnostic criteria with wider differences in the age groups over 70 years.
Conclusions: This study found no significant variation across periods but suggested a potential cohort effect. The influence of societal changes might moderate early life experiences across different generations with substantial impact on mental health in older age.
Keywords: China; cohort effect; meta-analysis; period; prevalence of dementia; temporal variation.
Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Ben-Shlomo Y, Kuh D. A life course approach to chronic disease epidemiology: conceptual models, empirical challenges and interdisciplinary perspectives. Int J Epidemiol. 2002;31:285–293. - PubMed
-
- Chan K, Wang W, Wu J, et al. Epidemiology of Alzheimer's disease and other forms of dementia in China, 1990–2010: a systematic review and analysis. Lancet. 2013;381:2016–2023. - PubMed
-
- Chang Y. Contemporary History in China. Taiwan: Tunghua; 1987.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

