[Construction and influence of human nuclear factor-κB p65 shRNA lentiviral vector on malignant biological behavior of lung cancer cells]
- PMID: 24854553
- PMCID: PMC6000443
- DOI: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2014.05.02
[Construction and influence of human nuclear factor-κB p65 shRNA lentiviral vector on malignant biological behavior of lung cancer cells]
Abstract
Background and objective: Nuclear factor-κB is an important transcription factor and is closely associated with a variety of malignant tumors. The biological behavior of lung tumor cells can be reversed by inhibiting the expression of NF-κBp65 directly or indirectly. Nuclear factor-κBp65 gene shRNA recombinant plasmids were constructed and then infected with A549 cells. New stable cell lines were selected, and the ability of migration and adhesion was identified.
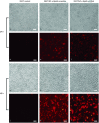
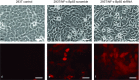
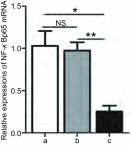
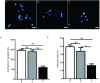
Methods: Both scramble control sequence and interference sequence (shRNA) of human nuclear factor-κBp65 were designed and synthesized to build recombinant plasmids, with BamH I site at the 5' end and Xho I and EcoR I sites at the 3' end. A549 cells were infected, and stable transfection strains were selected by puromycin. Western blot and qRT-PCR methods were applied to assess the interference efficient of NF-κBp65 and the protein expression level of IκBα. Transwell and MTT assays were carried out to analyze the ability of migration and adhesion of A549 cells separately.
Results: Recombinant plasmids were successfully built, and A549/NF-κB p65 scramble and A549/NF-κB p65 shRNA stable transfection strains were also successfully screened. Both mRNA and protein expression levels of NF-κBp65 showed that A549/NF-κBp65 shRNA cells decreased compared with A549/NF-κB p65 scramble cells and A549 cells, whereas the protein level of IκBα significantly increased. Both migration and adhesion abilities were also reduced.
Conclusions: In this study, both mRNA and protein expression levels of NF-κBp65 were effectively suppressed by RNA interference technique. NF-κBp65 inhibition can significantly reduce the migration and adhesion ability of A549 cells.
背景与目的 核因子-κB作为重要转录因子,与多种恶性肿瘤的发生发展有着密切联系,直接或间接抑制NF-κBp65的表达可逆转肿瘤细胞生物学行为。构建人核因子-κBp65基因shRNA重组质粒,感染A549细胞并筛选出稳定细胞株,对其迁移、粘附能力进行鉴定。方法 设计并合成人核因子-κBp65的乱序对照序列(scramble)和干扰序列(shRNA)构建重组质粒,在5’端引入一个BamHI位点,3’端引入一个XhoI位点和EcoRI位点;感染A549细胞并由嘌呤霉素做稳转株的筛选;应用Western blot、qRT-PCR技术检测NF-κBp65的干扰效果及IκBα蛋白表达水平的变化;Transwell、MTT法分析其对A549细胞迁移、粘附能力的影响。结果 成功构建重组质粒并筛选出A549/NF-κB p65 scramble稳转株和A549/NF-κB p65 shRNA稳转株;A549/NF-κB p65 shRNA稳转细胞株与A549/NF-κB p65 scramble稳转细胞株及A549细胞相比NF-κBp65的mRNA、蛋白表达水平均下调;IκBα蛋白水平明显下调;细胞迁移能力及粘附能力均降低。结论 本实验通过RNA干扰技术构建的重组慢病毒可有效抑制NF-κBp65 mRNA和蛋白的表达水平;抑制NF-κBp65可明显降低A549细胞的迁移和粘附能力。
Figures



References
-
- Gao N, Zhang XY, Jiang R, et al. Lentivirus-mediated RNA interference and over-expression of CDK2AP1 CDNA regulate CDK2AP1 expression in human lung cancer A549 cells. Chem Res. 2011;27(3):445–449.
-
- Guo HJ, Zhu GF. Role of NF-κB signaling pathway in lung cancer. http://med.wanfangdata.com.cn/Paper/Detail/PeriodicalPaper_gwyx-hxxt2013... Guoji Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2013;33(18):1402–1406.
- 郭 红娟, 朱 光发. 核因子-κB信号通路在肺癌中的作用. http://med.wanfangdata.com.cn/Paper/Detail/PeriodicalPaper_gwyx-hxxt2013... 国际呼吸杂志. 2013;33(18):1402–1406.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

