Effects of acclimation salinity on the expression of selenoproteins in the tilapia, Oreochromis mossambicus
- PMID: 24854764
- PMCID: PMC4082732
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2014.04.003
Effects of acclimation salinity on the expression of selenoproteins in the tilapia, Oreochromis mossambicus
Abstract
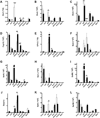
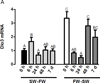
Selenoproteins are ubiquitously expressed, act on a variety of physiological redox-related processes, and are mostly regulated by selenium levels in animals. To date, the expression of most selenoproteins has not been verified in euryhaline fish models. The Mozambique tilapia, Oreochromis mossambicus, a euryhaline cichlid fish, has a high tolerance for changes in salinity and survives in fresh water (FW) and seawater (SW) environments which differ greatly in selenium availability. In the present study, we searched EST databases for cichlid selenoprotein mRNAs and screened for their differential expression in FW and SW-acclimated tilapia. The expression of mRNAs encoding iodothyronine deiodinases 1, 2 and 3 (Dio1, Dio2, Dio3), Fep15, glutathione peroxidase 2, selenoproteins J, K, L, M, P, S, and W, was measured in the brain, eye, gill, kidney, liver, pituitary, muscle, and intraperitoneal white adipose tissue. Gene expression of selenophosphate synthetase 1, Secp43, and selenocysteine lyase, factors involved in selenoprotein synthesis or in selenium metabolism, were also measured. The highest variation in selenoprotein and synthesis factor mRNA expression between FW- and SW-acclimated fish was found in gill and kidney. While the branchial expression of Dio3 was increased upon transferring tilapia from SW to FW, the inverse effect was observed when fish were transferred from FW to SW. Protein content of Dio3 was higher in fish acclimated to FW than in those acclimated to SW. Together, these results outline tissue distribution of selenoproteins in FW and SW-acclimated tilapia, and indicate that at least Dio3 expression is regulated by environmental salinity.
Keywords: Acclimation salinity; Euryhaline; Fish; Selenium; Selenoprotein; Tilapia.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier GmbH. All rights reserved.
Figures
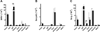

Similar articles
-
Regulation of thyroid hormones and branchial iodothyronine deiodinases during freshwater acclimation in tilapia.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2021 Dec 1;538:111450. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2021.111450. Epub 2021 Sep 7. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2021. PMID: 34506867 Free PMC article.
-
Differential effects of cortisol and 11-deoxycorticosterone on ion transport protein mRNA levels in gills of two euryhaline teleosts, Mozambique tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) and striped bass (Morone saxatilis).J Endocrinol. 2011 Apr;209(1):115-26. doi: 10.1530/JOE-10-0326. Epub 2011 Jan 31. J Endocrinol. 2011. PMID: 21282254
-
The effects of transfer from steady-state to tidally-changing salinities on plasma and branchial osmoregulatory variables in adult Mozambique tilapia.Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2019 Jan;227:134-145. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2018.10.005. Epub 2018 Oct 11. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30315867 Free PMC article.
-
Endocrine and osmoregulatory responses to tidally-changing salinities in fishes.Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2022 Sep 15;326:114071. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2022.114071. Epub 2022 Jun 11. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2022. PMID: 35697315 Review.
-
The diverse role of selenium within selenoproteins: a review.J Am Diet Assoc. 1999 Jul;99(7):836-43. doi: 10.1016/S0002-8223(99)00198-4. J Am Diet Assoc. 1999. PMID: 10405682 Review.
Cited by
-
Selenium Deficiency Leads to Changes in Renal Fibrosis Marker Proteins and Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway Components.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2022 Mar;200(3):1127-1139. doi: 10.1007/s12011-021-02730-1. Epub 2021 Apr 24. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2022. PMID: 33895963
-
Transcriptome analysis of the brain provides insights into the regulatory mechanism for Coilia nasus migration.BMC Genomics. 2020 Jun 18;21(1):410. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-06816-3. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32552858 Free PMC article.
-
Selenocysteine β-Lyase: Biochemistry, Regulation and Physiological Role of the Selenocysteine Decomposition Enzyme.Antioxidants (Basel). 2019 Sep 1;8(9):357. doi: 10.3390/antiox8090357. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31480609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of thyroid hormones and branchial iodothyronine deiodinases during freshwater acclimation in tilapia.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2021 Dec 1;538:111450. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2021.111450. Epub 2021 Sep 7. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2021. PMID: 34506867 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wen H, Carignan J. Ocean to continent transfer of atmospheric Se as revealed by epiphytic lichens. Environ Pollut. 2009;157(10):2790–2797. - PubMed
-
- Nriagu J. A global assessment of natural sources of atmospheric trace metals. Nature. 1989;338:47–49.
-
- Squires JE, Berry MJ. Eukaryotic selenoprotein synthesis: mechanistic insight incorporating new factors and new functions for old factors. IUBMB Life. 2008;60(4):232–235. - PubMed
-
- Low SC, Harney JW, Berry MJ. Cloning and functional characterization of human selenophosphate synthetase, an essential component of selenoprotein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1995;270(37):21659–21664. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

