Nonlinear analysis of saccade speed fluctuations during combined action and perception tasks
- PMID: 24854830
- PMCID: PMC4164043
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2014.05.010
Nonlinear analysis of saccade speed fluctuations during combined action and perception tasks
Abstract
Background: Saccades are rapid eye movements used to gather information about a scene which requires both action and perception. These are usually studied separately, so that how perception influences action is not well understood. In a dual task, where the subject looks at a target and reports a decision, subtle changes in the saccades might be caused by action-perception interactions. Studying saccades might provide insight into how brain pathways for action and for perception interact.
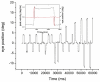
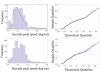
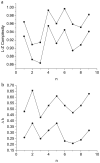
New method: We applied two complementary methods, multifractal detrended fluctuation analysis and Lempel-Ziv complexity index to eye peak speed recorded in two experiments, a pure action task and a combined action-perception task.
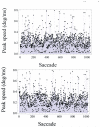
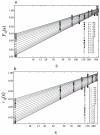
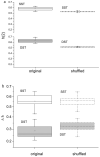
Results: Multifractality strength is significantly different in the two experiments, showing smaller values for dual decision task saccades compared to simple-task saccades. The normalized Lempel-Ziv complexity index behaves similarly i.e. is significantly smaller in the decision saccade task than in the simple task.
Comparison with existing methods: Compared to the usual statistical and linear approaches, these analyses emphasize the character of the dynamics involved in the fluctuations and offer a sensitive tool for quantitative evaluation of the multifractal features and of the complexity measure in the saccades peak speeds when different brain circuits are involved.
Conclusion: Our results prove that the peak speed fluctuations have multifractal characteristics with lower magnitude for the multifractality strength and for the complexity index when two neural pathways are simultaneously activated, demonstrating the nonlinear interaction in the brain pathways for action and perception.
Keywords: Action–perception task; Lempel–Ziv complexity; Multifractal properties; Saccade speed peak.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Aboy M, Hornero R, Abásolo D, Alvarez D. Interpretation of the Lempel-Ziv complexity measure in the context of biomedical signal analysis. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2006;53:2282–8. - PubMed
-
- Amigo JM, Szczepaski J, Wajnryb E, Sanchez-Vives MV. Estimating the entropy rate of spike trains via Lempel-Ziv complexity. Neural Comput. 2004;16:717–36. - PubMed
-
- Ausloos M. Measuring complexity with multifractals in texts. Translation effects. Chaos Soliton Fract. 2012;45:1349–57.
-
- Chaitin GJ. On the length of programs for computing finite binary sequences. J ACMS. 1966;13(4):547–69.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

