Transposon-mediated targeted and specific knockdown of maternally expressed transcripts in the ascidian Ciona intestinalis
- PMID: 24854849
- PMCID: PMC4031475
- DOI: 10.1038/srep05050
Transposon-mediated targeted and specific knockdown of maternally expressed transcripts in the ascidian Ciona intestinalis
Abstract
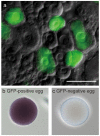
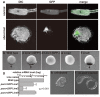
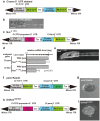
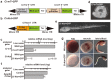
Maternal mRNAs play crucial roles during early embryogenesis of ascidians, but their functions are largely unknown. In this study, we developed a new method to specifically knockdown maternal mRNAs in Ciona intestinalis using transposon-mediated transgenesis. We found that GFP expression is epigenetically silenced in Ciona intestinalis oocytes and eggs, and this epigenetic silencing of GFP was used to develop the knockdown method. When the 5' upstream promoter and 5' untranslated region (UTR) of a maternal gene are used to drive GFP in eggs, the maternal gene is specifically knocked down together with GFP. The 5' UTR of the maternal gene is the major element that determines the target gene silencing. Zygotic transcription of the target gene is unaffected, suggesting that the observed phenotypes specifically reflect the maternal function of the gene. This new method can provide breakthroughs in studying the functions of maternal mRNAs.
Figures

Similar articles
-
piRNA-like small RNAs are responsible for the maternal-specific knockdown in the ascidian Ciona intestinalis Type A.Sci Rep. 2018 Apr 12;8(1):5869. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-24319-w. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29651003 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal factor-mediated epigenetic gene silencing in the ascidian Ciona intestinalis.Mol Genet Genomics. 2010 Jan;283(1):99-110. doi: 10.1007/s00438-009-0500-4. Epub 2009 Nov 28. Mol Genet Genomics. 2010. PMID: 19946786
-
Germline Transgenesis in Ciona.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1029:109-119. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-7545-2_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 29542084
-
Germline transgenesis and insertional mutagenesis in the ascidian Ciona intestinalis.Dev Dyn. 2007 Jul;236(7):1758-67. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.21111. Dev Dyn. 2007. PMID: 17342755 Review.
-
Transposon mediated transgenesis in a marine invertebrate chordate: Ciona intestinalis.Genome Biol. 2007;8 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S3. doi: 10.1186/gb-2007-8-s1-s3. Genome Biol. 2007. PMID: 18047695 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
piRNA-like small RNAs are responsible for the maternal-specific knockdown in the ascidian Ciona intestinalis Type A.Sci Rep. 2018 Apr 12;8(1):5869. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-24319-w. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29651003 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Conklin E. G. Organ forming substances in the eggs of ascidians. Biol. Bull. 8, 205–230 (1905).
-
- Nishida H. Specification of embryonic axis and mosaic development in ascidians. Dev. Dyn. 233, 1177–1193 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Nishida H. & Sawada K. macho-1 encodes a localized mRNA in ascidian eggs that specifies muscle fate during embryogenesis. Nature 409, 679–680 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Nishiyama A. & Fujiwara S. RNA interference by expressing short hairpin RNA in the Ciona intestinalis embryo. Dev. Growth Differ. 50, 521–529 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Satou Y., Imai K. S. & Satoh N. Action of morpholinos in Ciona embryos. Genesis 30, 103–106 (2001). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

