Effects of extended-release niacin/laropiprant, simvastatin, and the combination on correlations between apolipoprotein B, LDL cholesterol, and non-HDL cholesterol in patients with dyslipidemia
- PMID: 24855368
- PMCID: PMC4019613
- DOI: 10.2147/VHRM.S58694
Effects of extended-release niacin/laropiprant, simvastatin, and the combination on correlations between apolipoprotein B, LDL cholesterol, and non-HDL cholesterol in patients with dyslipidemia
Abstract
Background: Statins modify correlations between apolipoprotein B (apoB) and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and apoB and non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C); however, it is not known whether niacin-based therapies have similar effects.
Objective: To evaluate the effects of extended-release niacin (ERN)/laropiprant (LRPT), simvastatin (SIMVA), and ERN/LRPT + SIMVA (pooled ERN/LRPT + SIMVA) on apoB:LDL-C and apoB:non-HDL-C correlations in dyslipidemic patients.
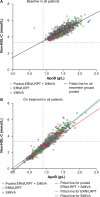
Methods: This post-hoc analysis of a 12-week study evaluated the apoB:LDL-C and apoB:non-HDL-C correlations in dyslipidemic patients randomized equally to double-blind ERN/LRPT 1 g/20 mg, SIMVA 10, 20, or 40 mg, or ERN/LRPT 1 g/20 mg + SIMVA (10, 20, or 40 mg) once daily for 4 weeks. At week 5, doses were doubled in all groups except SIMVA 40 mg (unchanged) and ERN/LRPT 1 g/20 mg + SIMVA 40 mg (switched to ERN/LRPT 2 g/40 mg + SIMVA 40 mg). Simple linear regression analyses were used to calculate LDL-C and non-HDL-C levels corresponding to known apoB baseline values (ie, in untreated patients) and following treatment.
Results: The apoB:LDL-C and apoB:non-HDL-C correlations were higher and the predicted LDL-C and non-HDL-C levels for a known apoB value were considerably lower following treatment with ERN/LRPT, SIMVA and ERN/LRPT + SIMVA compared with untreated patients at baseline.
Conclusion: Greater dissociation of apoB, LDL-C, and non-HDL-C targets occur following treatment with ERN/LRPT, SIMVA, and ERN/LRPT + SIMVA in patients with dyslipidemia. The achievement of more aggressive LDL-C and non-HDL-C goals in patients receiving lipid-modifying therapy may further reduce coronary risk by normalizing apoB-containing atherogenic lipoproteins.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00269217.
Keywords: LDL-C; apoB; non-HDL-C.
Figures
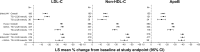

Similar articles
-
Effects of extended-release niacin/laropiprant on correlations between apolipoprotein B, LDL-cholesterol and non-HDL-cholesterol in patients with type 2 diabetes.Lipids Health Dis. 2016 Jul 12;15(1):116. doi: 10.1186/s12944-016-0282-8. Lipids Health Dis. 2016. PMID: 27405296 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Extended-Release Niacin on High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL) Functionality, Lipoprotein Metabolism, and Mediators of Vascular Inflammation in Statin-Treated Patients.J Am Heart Assoc. 2015 Sep 15;4(9):e001508. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.114.001508. J Am Heart Assoc. 2015. PMID: 26374297 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of coadministered extended-release niacin/laropiprant and simvastatin on lipoprotein subclasses in patients with dyslipidemia.J Clin Lipidol. 2012 May-Jun;6(3):235-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2011.11.004. Epub 2011 Dec 3. J Clin Lipidol. 2012. PMID: 22658147 Clinical Trial.
-
Pitavastatin: novel effects on lipid parameters.Atheroscler Suppl. 2011 Nov;12(3):277-84. doi: 10.1016/S1567-5688(11)70887-X. Atheroscler Suppl. 2011. PMID: 22152282 Review.
-
Targeting low HDL-cholesterol to decrease residual cardiovascular risk in the managed care setting.J Manag Care Pharm. 2008 Oct;14(8 Suppl):S3-28; quiz S30-1. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2008.14.S8-A.1. J Manag Care Pharm. 2008. PMID: 19891279 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dyslipidemia in Special Ethnic Populations.Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2016 Mar;45(1):205-16. doi: 10.1016/j.ecl.2015.09.013. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2016. PMID: 26893006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dyslipidemia in special ethnic populations.Cardiol Clin. 2015 May;33(2):325-33. doi: 10.1016/j.ccl.2015.01.005. Cardiol Clin. 2015. PMID: 25939303 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Cow, Donkey and Goat Milk Extracellular Vesicles as Revealed by Metabolomic Profile.Nutrients. 2020 Sep 23;12(10):2908. doi: 10.3390/nu12102908. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32977543 Free PMC article.
-
Low High-Density Lipoprotein and Risk of Myocardial Infarction.Clin Med Insights Cardiol. 2015 Dec 3;9:113-7. doi: 10.4137/CMC.S26624. eCollection 2015. Clin Med Insights Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 26692765 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Management of Severe Hypertriglyceridemia in Pregnancy With Niacin: Reevaluating Safety and Therapeutic Benefits.Case Rep Endocrinol. 2025 Jan 30;2025:2644678. doi: 10.1155/crie/2644678. eCollection 2025. Case Rep Endocrinol. 2025. PMID: 39949380 Free PMC article.
References
-
- National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) final report. Circulation. 2002;106:3143–3421. - PubMed
-
- Stone NJ, Robinson J, Lichtenstein AH, et al. ACC/AHA Guideline on the Treatment of Blood Cholesterol to Reduce Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Risk in Adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013 2013 Nov 7; Epub. - PubMed
-
- Brunzell JD, Davidson M, Furberg CD, et al. Lipoprotein management in patients with cardiometabolic risk: consensus statement from the American Diabetes Association and the American College of Cardiology Foundation. Diabetes Care. 2008;31:811–822. - PubMed
-
- Davidson MH, Ballantyne CM, Jacobson TA, et al. Clinical utility of inflammatory markers and advanced lipoprotein testing: advice from an expert panel of lipid specialists. J Clin Lipidol. 2011;5:338–367. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

