2-(5-Chloro-2-oxoindolin-3-yl-idene)hydrazinecarbo-thio-amide
- PMID: 24855470
- PMCID: PMC4029216
- DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813033369
2-(5-Chloro-2-oxoindolin-3-yl-idene)hydrazinecarbo-thio-amide
Abstract
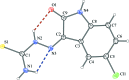
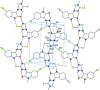
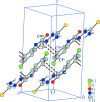
The title mol-ecule, C9H7ClN4OS, is almost planar, with an r.m.s. deviation of 0.034 (2) Å for the mean plane through all the non-H atoms. Intra-molecular N-H⋯O and N-H⋯N hydrogen bonds form S(6) and S(5) ring motifs, respectively. In the crystal, mol-ecules are assembled into inversion dimers through pairs of co-operative N-H⋯Cl inter-actions. These dimers are connected along the b axis by N-H⋯O and N-H⋯S hydrogen bonds, generating layers parallel to (103). The layers are further connected along the a axis into a three-dimensional network, through weak π-π stacking inter-actions [centroid-centroid distance = 3.849 (2) Å].
Figures
References
-
- Brandenburg, K. (2006). DIAMOND Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
-
- Bruker (2009). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Cerchiaro, G. & Ferreira, A. M. C. (2006). J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 17, 1473–1485.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
