Non-choroidal yellow melanoma showing positive staining with Sudan Black consistent with the presence of lipofuscin: a case report
- PMID: 24855574
- PMCID: PMC4029254
- DOI: 10.5826/dpc.0402a09
Non-choroidal yellow melanoma showing positive staining with Sudan Black consistent with the presence of lipofuscin: a case report
Abstract
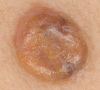
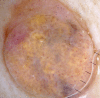
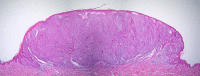
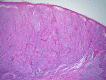
A case of a predominantly yellow primary superficial spreading melanoma arising on the back of a 44-year-old woman is presented. Possible causes of the clinical and dermatoscopic yellow color are discussed. Staining with the histochemical stain, Sudan Black, revealed a differential uptake compared to a closely matched control melanoma. We speculate that the clinical and dermatoscopic yellow color could be due to the presence of increased amounts of the pigment lipofuscin, which is known to produce subtle orange color in some choroidal melanomas.
Keywords: Sudan Black; dermatopathology; dermatoscopy; dermoscopy; hypomelanotic melanoma; lipofuscin; yellow melanoma.
Figures
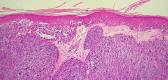
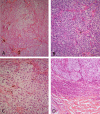

References
-
- Rosendahl C, Cameron A, McColl I, Wilkinson D. Dermatoscopy in routine practice—“Chaos and Clues.”. Aust Fam Physician. 2012 Jul;41(7):482–7. - PubMed
-
- Chamberlain AJ, Fritschi L, Kelly JW. Nodular melanoma: patients’ perceptions of presenting features and implications for earlier detection. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003 May;48(5):694–701. - PubMed
-
- Moloney FJ, Menzies SW. Key points in the dermoscopic diagnosis of hypomelanotic melanoma and nodular melanoma. J Dermatol. 2011 Jan;38(1):10–5. - PubMed
-
- Kittler H. Dermatoscopy: introduction of a new algorithmic method based on pattern analysis for diagnosis of pigmented skin lesions. Dermatopathology: Practical & Conceptual. 2007;13:3.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
