The effect of early neuromuscular electrical stimulation therapy in acute/subacute ischemic stroke patients with Dysphagia
- PMID: 24855608
- PMCID: PMC4026600
- DOI: 10.5535/arm.2014.38.2.153
The effect of early neuromuscular electrical stimulation therapy in acute/subacute ischemic stroke patients with Dysphagia
Abstract
Objective: To compare the outcome of an early application of neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) combined with traditional dysphagia therapy (TDT) versus traditional dysphagia therapy only in acute/subacute ischemic stroke patients with moderate to severe dysphagia by videofluoroscopic swallowing study (VFSS).
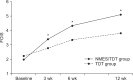
Methods: Fifty-seven dysphagic stroke patients were enrolled in a VFSS within 10 days after stroke onset. Patients were randomly assigned into two treatment groups. Thirty-one patients received NMES combined with TDT (NMES/TDT group) and 26 patients received TDT only (TDT group). Electrical stimulation with a maximal tolerable intensity was applied on both suprahyoid muscles for 30 minutes, 5 days per week during 3 weeks. The swallowing function was evaluated at baseline and 3, 6, and 12 weeks after baseline. Outcomes of the VFSS were assessed using the Functional Oral Intake Scale (FOIS).
Results: The mean ages were 63.5±11.4 years in the NMES/TDT group and 66.7±9.5 years in the TDT group. Both groups showed a significant improvement on the FOIS after treatment. The FOIS score was significantly more improved at 3 and 6 weeks after baseline in the NMES/TDT group than in the TDT group (p<0.05).
Conclusion: An early application of NMES combined with TDT showed a positive effect in acute/subacute ischemic stroke patients with dysphagia. These results indicated that the early application of NMES could be used as a supplementary treatment of TDT to help rehabilitate acute/subacute dysphagic stroke patients by improving their swallowing coordination.
Keywords: Acute stroke; Dysphagia; Neuromuscular electrical stimulation.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

References
-
- Daniels SK, Brailey K, Priestly DH, Herrington LR, Weisberg LA, Foundas AL. Aspiration in patients with acute stroke. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1998;79:14–19. - PubMed
-
- Roth EJ, Lovell L, Harvey RL, Heinemann AW, Semik P, Diaz S. Incidence of and risk factors for medical complications during stroke rehabilitation. Stroke. 2001;32:523–529. - PubMed
-
- Horner J, Massey EW. Silent aspiration following stroke. Neurology. 1988;38:317–319. - PubMed
-
- Teasell RW, Bach D, McRae M. Prevalence and recovery of aspiration poststroke: a retrospective analysis. Dysphagia. 1994;9:35–39. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

