Defining estrogenic mechanisms of bisphenol A analogs through high throughput microscopy-based contextual assays
- PMID: 24856822
- PMCID: PMC4301571
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2014.03.013
Defining estrogenic mechanisms of bisphenol A analogs through high throughput microscopy-based contextual assays
Abstract
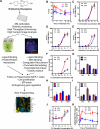
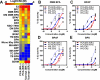
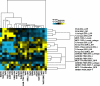
Environmental exposures to chemically heterogeneous endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) mimic or interfere with hormone actions and negatively affect human health. Despite public interest and the prevalence of EDCs in the environment, methods to mechanistically classify these diverse chemicals in a high throughput (HT) manner have not been actively explored. Here, we describe the use of multiparametric, HT microscopy-based platforms to examine how a prototypical EDC, bisphenol A (BPA), and 18 poorly studied BPA analogs (BPXs), affect estrogen receptor (ER). We show that short exposure to BPA and most BPXs induces ERα and/or ERβ loading to DNA changing target gene transcription. Many BPXs exhibit higher affinity for ERβ and act as ERβ antagonists, while they act largely as agonists or mixed agonists and antagonists on ERα. Finally, despite binding to ERs, some BPXs exhibit lower levels of activity. Our comprehensive view of BPXs activities allows their classification and the evaluation of potential harmful effects. The strategy described here used on a large-scale basis likely offers a faster, more cost-effective way to identify safer BPA alternatives.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures



Comment in
-
Casting a wide net for endocrine disruptors.Chem Biol. 2014 Jun 19;21(6):705-6. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2014.06.002. Chem Biol. 2014. PMID: 24950102
References
-
- Borras M, Laios I, El Khissiin A, Seo HS, Lempereur F, Legros N, Leclercq G. Estrogenic and antiestrogenic regulation of the half-life of covalently labeled estrogen receptor in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1996;57:203–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- ES023512-01/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- HD007495/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 ES018789/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HD007495/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD007495/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA125123/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056338/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK56338/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 HD007495/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01ES023206-01/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- CA125123/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES023206/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES023512/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- 1RC2ES018789-01/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

