SHIP1 regulates MSC numbers and their osteolineage commitment by limiting induction of the PI3K/Akt/β-catenin/Id2 axis
- PMID: 24857423
- PMCID: PMC4172390
- DOI: 10.1089/scd.2014.0122
SHIP1 regulates MSC numbers and their osteolineage commitment by limiting induction of the PI3K/Akt/β-catenin/Id2 axis
Abstract
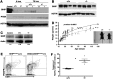
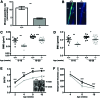
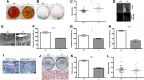
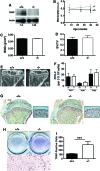
Here, we show that Src homology 2-domain-containing inositol 5'-phosphatase 1 (SHIP1) is required for the efficient development of osteoblasts from mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) such that bone growth and density are reduced in mice that lack SHIP1 expression in MSCs. We find that SHIP1 promotes the osteogenic output of MSCs by limiting activation of the PI3K/Akt/β-catenin pathway required for induction of the MSC stemness factor Id2. In parallel, we demonstrate that mice with myeloid-restricted ablation of SHIP1, including osteoclasts (OCs), show no reduction in bone mass or density. Hence, diminished bone mass and density in the SHIP1-deficient mice results from SHIP deficiency in MSC and osteolineage progenitors. Intriguingly, mice with a SHIP-deficient MSC compartment also exhibit decreased OC numbers. In agreement with our genetic findings we also show that treatment of mice with an SHIP1 inhibitor (SHIPi) significantly reduces bone mass. These findings demonstrate a novel role for SHIP1 in MSC fate determination and bone growth. Further, SHIPi may represent a novel therapeutic approach to limit bone development in osteopetrotic and sclerotic bone diseases.
Figures



Similar articles
-
SHIP1-expressing mesenchymal stem cells regulate hematopoietic stem cell homeostasis and lineage commitment during aging.Stem Cells Dev. 2015 May 1;24(9):1073-81. doi: 10.1089/scd.2014.0501. Epub 2015 Feb 5. Stem Cells Dev. 2015. PMID: 25525673 Free PMC article.
-
Role of SHIP1 in bone biology.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2013 Mar;1280:11-4. doi: 10.1111/nyas.12091. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2013. PMID: 23551095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Leukemia-associated mutations in SHIP1 inhibit its enzymatic activity, interaction with the GM-CSF receptor and Grb2, and its ability to inactivate PI3K/AKT signaling.Cell Signal. 2012 Nov;24(11):2095-101. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2012.07.017. Epub 2012 Jul 20. Cell Signal. 2012. PMID: 22820502
-
Src homology 2 domain-containing inositol-5-phosphatase 1 (SHIP1) negatively regulates TLR4-mediated LPS response primarily through a phosphatase activity- and PI-3K-independent mechanism.Blood. 2005 Jun 15;105(12):4685-92. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-01-0191. Epub 2005 Feb 8. Blood. 2005. PMID: 15701712
-
SHIP1 and its role for innate immune regulation-Novel targets for immunotherapy.Eur J Immunol. 2023 Dec;53(12):e2350446. doi: 10.1002/eji.202350446. Epub 2023 Oct 27. Eur J Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37742135 Review.
Cited by
-
A small-molecule inhibitor of SHIP1 reverses age- and diet-associated obesity and metabolic syndrome.JCI Insight. 2016 Jul 21;1(11):e88544. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.88544. JCI Insight. 2016. PMID: 27536730 Free PMC article.
-
SHIPi Enhances Autologous and Allogeneic Hematolymphoid Stem Cell Transplantation.EBioMedicine. 2015 Mar 1;2(3):205-213. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2015.02.004. EBioMedicine. 2015. PMID: 26052545 Free PMC article.
-
What happens to the osteoporotic bone mesenchymal stem cells? Evidence from RNA sequencing.Int J Med Sci. 2024 Jan 1;21(1):95-106. doi: 10.7150/ijms.88146. eCollection 2024. Int J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38164361 Free PMC article.
-
SHIP1-expressing mesenchymal stem cells regulate hematopoietic stem cell homeostasis and lineage commitment during aging.Stem Cells Dev. 2015 May 1;24(9):1073-81. doi: 10.1089/scd.2014.0501. Epub 2015 Feb 5. Stem Cells Dev. 2015. PMID: 25525673 Free PMC article.
-
SHIP prevents metastasis.Aging (Albany NY). 2016 May;8(5):837-8. doi: 10.18632/aging.100964. Aging (Albany NY). 2016. PMID: 27208543 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Hadjidakis DJ. and Androulakis I. (2006). Bone remodeling. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1092:385–396 - PubMed
-
- Friedenstein AJ, Petrakova KV, Kurolesova AI. and Frolova GP. (1968). Heterotopic of bone marrow. Analysis of precursor cells for osteogenic and hematopoietic tissues. Transplantation 6:230–247 - PubMed
-
- Friedenstein AJ, Deriglasova UF, Kulagina NN, Panasuk AF, Rudakowa SF, Luria EA. and Ruadkow IA. (1974). Precursors for fibroblasts in different populations of hematopoietic cells as detected by the in vitro colony assay method. Exp Hematol 2:83–92 - PubMed
-
- Owen M. and Friedenstein AJ. (1988). Stromal stem cells: marrow-derived osteogenic precursors. Ciba Found Symp 136:42–60 - PubMed
-
- Caplan AI. (1991). Mesenchymal stem cells. J Orthop Res 9:641–650 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
