New applications for phage integrases
- PMID: 24857859
- PMCID: PMC4111918
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2014.05.014
New applications for phage integrases
Abstract
Within the last 25 years, bacteriophage integrases have rapidly risen to prominence as genetic tools for a wide range of applications from basic cloning to genome engineering. Serine integrases such as that from ϕC31 and its relatives have found an especially wide range of applications within diverse micro-organisms right through to multi-cellular eukaryotes. Here, we review the mechanisms of the two major families of integrases, the tyrosine and serine integrases, and the advantages and disadvantages of each type as they are applied in genome engineering and synthetic biology. In particular, we focus on the new areas of metabolic pathway construction and optimization, biocomputing, heterologous expression and multiplexed assembly techniques. Integrases are versatile and efficient tools that can be used in conjunction with the various extant molecular biology tools to streamline the synthetic biology production line.
Keywords: bacteriophages; genome engineering; integrases; integrating vectors; synthetic biology.
Copyright © 2014. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures
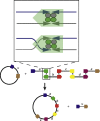
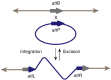
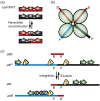



References
-
- Suttle C.A. Marine viruses—major players in the global ecosystem. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2007;5:801–812. - PubMed
-
- Hambly E., Suttle C.A. The viriosphere, diversity, and genetic exchange within phage communities. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2005;8:444–450. - PubMed
-
- Ptashne M. 3rd ed. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; Cold Spring Harbor, NY: 2004. A genetic switch: phage lambda revisited.
-
- Smith M.C.M. Conservative site-specific recombination. In: Lennarz W.J., Lane M.D., editors. vol. 1. Academic Press; Waltham, MA: 2013. pp. 555–561. (Encyclopedia of Biological Chemistry).
-
- Campbell A.M. Episomes. Adv Genet Inc Mol Genet Med. 1962;11:101–145.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

