Vitamin D supplementation of breastfed infants: a randomized dose-response trial
- PMID: 24858141
- PMCID: PMC4104134
- DOI: 10.1038/pr.2014.76
Vitamin D supplementation of breastfed infants: a randomized dose-response trial
Abstract
Background: Breastfed infants require supplementation with vitamin D (vD), but little is known about the necessary dose. This double blind trial evaluated four different doses of vD.
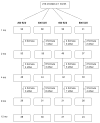
Methods: Exclusively breastfed infants (N = 213) were randomized at 1 mo to one of four doses, which they received through 9 mo while receiving no formula. The supplements provided daily 200 IU, 400 IU, 600 IU, or 800 IU of vD. The primary endpoint was plasma 25(OH)D level, and secondary outcomes were plasma parathyroid hormone and calcium, and illness incidence. The study was conducted during winter at 41° N.
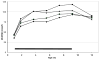
Results: Most infants had low (<50 nmol/l) 25(OH)D levels at 1 mo, but with supplementation levels rose. Overall, levels of 25(OH)D differed significantly in proportion to vD dose. There were no effects of vD on illness incidence or growth. Low levels were common, with 7.8% of levels being <50 nmol/l and 15 infants having 2 to 4 low levels.
Conclusion: The four doses of vD produced different plasma levels of 25(OH)D. The higher doses were somewhat more efficacious in maintaining vD sufficiency in breastfed infants. The findings support the recommended dose of 400 IU/d, and stress the need to start supplementation at birth.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00494104.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Holick MF. Vitamin D deficiency. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:266–81. - PubMed
-
- Institute of Medicine. Dietary reference intakes for calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, vitamin D, and fluoride. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press; 1997. - PubMed
-
- Specker BL, Tsang RC, Hollis BW. Effect of race and diet on human-milk vitamin D and 25-hydroxyvitamin D. Am J Dis Child. 1985;139:1134–7. - PubMed
-
- Hollis BW, Pittard WB, Reinhardt TA. Relationships among vitamin D, 25-hydroxyvitamin D, and vitamin D-binding protein concentrations in the plasma and milk of human subjects. J Clin Endocinol Metab. 1986;62:41–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

