Diagnosis and treatment of fetal arrhythmia
- PMID: 24858320
- PMCID: PMC4073210
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0034-1372430
Diagnosis and treatment of fetal arrhythmia
Abstract
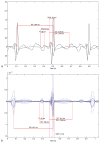
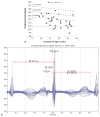
Aims: Detection and careful stratification of fetal heart rate (FHR) is extremely important in all pregnancies. The most lethal cardiac rhythm disturbances occur during apparently normal pregnancies where FHR and rhythm are regular and within normal or low-normal ranges. These hidden depolarization and repolarization abnormalities, associated with genetic ion channelopathies cannot be detected by echocardiography, and may be responsible for up to 10% of unexplained fetal demise, prompting a need for newer and better fetal diagnostic techniques. Other manifest fetal arrhythmias such as premature beats, tachycardia, and bradycardia are commonly recognized.
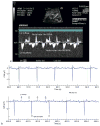
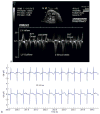
Methods: Heart rhythm diagnosis in obstetrical practice is usually made by M-mode and pulsed Doppler fetal echocardiography, but not all fetal cardiac time intervals are captured by echocardiographic methods.
Results and conclusions: This article reviews different types of fetal arrhythmias, their presentation and treatment strategies, and gives an overview of the present and future diagnostic techniques.
Thieme Medical Publishers 333 Seventh Avenue, New York, NY 10001, USA.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Cuneo is an educational consultant for Philips Ultrasound.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Fetal cardiac arrhythmia detection and in utero therapy.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2010 May;7(5):277-90. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2010.32. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2010. PMID: 20418904 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Echocardiographic evaluation of fetal arrhythmias.Kardiol Pol. 1990 Feb;33(2):136-49. Kardiol Pol. 1990. PMID: 2277485 English, Polish.
-
The Incremental Benefit of Color Tissue Doppler in Fetal Arrhythmia Assessment.J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2019 Jan;32(1):145-156. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2018.08.009. Epub 2018 Oct 16. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2019. PMID: 30340890
-
Arrhythmia and structural abnormalities of the fetal heart.Br Heart J. 1983 Dec;50(6):550-4. doi: 10.1136/hrt.50.6.550. Br Heart J. 1983. PMID: 6651998 Free PMC article.
-
[Fetal arrhythmias].Duodecim. 2014;130(2):152-60. Duodecim. 2014. PMID: 24605430 Review. Finnish.
Cited by
-
Fetal Bradycardia Caused by Monogenic Disorders-A Review of the Literature.J Clin Med. 2022 Nov 22;11(23):6880. doi: 10.3390/jcm11236880. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36498454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiotocography and beyond: a review of one-dimensional Doppler ultrasound application in fetal monitoring.Physiol Meas. 2018 Aug 14;39(8):08TR01. doi: 10.1088/1361-6579/aad4d1. Physiol Meas. 2018. PMID: 30027897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Case of Fetal Tachycardia after Electroconvulsive Therapy: A Possible Effect of Maternal Hypoxia and Uterine Contractions.Case Rep Psychiatry. 2019 Jul 4;2019:3709612. doi: 10.1155/2019/3709612. eCollection 2019. Case Rep Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 31355037 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and genetic spectrum of neonatal arrhythmia in a NICU.Transl Pediatr. 2021 Oct;10(10):2432-2438. doi: 10.21037/tp-21-233. Transl Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34765466 Free PMC article.
-
Persistent Fetal SVT in a COVID-19 Positive Pregnancy.Case Rep Obstet Gynecol. 2022 Jan 7;2022:9933520. doi: 10.1155/2022/9933520. eCollection 2022. Case Rep Obstet Gynecol. 2022. PMID: 35013695 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Oudijk MA. Fetal Tachycardia: Diagnosis and Treatment and the Fetal QT Interval in Hypoxia. Vol. 216 Utrecht, The Netherlands: Dong UMC, Neoventa Medical AB, Stiefel; 2003.
-
- Dubin AM, Cuneo BF, Strasburger JF, Wakai RT, Van Hare GF, Rosenthal DN. Congenital junctional ectopic tachycardia and congenital complete atrioventricular block: a shared etiology? Heart Rhythm. 2005;2(3):313–315. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

