Hepatitis B virus replication is blocked by a 2-hydroxyisoquinoline-1,3(2H,4H)-dione (HID) inhibitor of the viral ribonuclease H activity
- PMID: 24858512
- PMCID: PMC4101055
- DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2014.05.007
Hepatitis B virus replication is blocked by a 2-hydroxyisoquinoline-1,3(2H,4H)-dione (HID) inhibitor of the viral ribonuclease H activity
Abstract
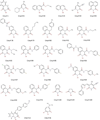
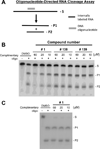
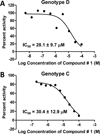
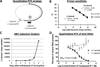
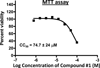
Nucleos(t)ide analog drugs profoundly suppress Hepatitis B virus (HBV) replication but rarely cure the infection, so therapy is usually life-long. The nucleos(t)ide analogs inhibit the viral DNA polymerase and often push HBV to the brink of extinction, so it may be possible to eradicate HBV by suppressing HBV replication further. The HBV ribonuclease H (RNaseH) is a logical new drug target because it is the second of only two viral enzymes essential for viral replication. We recently developed a low throughput screening pipeline for inhibitors of the HBV RNaseH and viral replication. Here, we screened a series of twenty-three nitrogen-based polyoxygenated heterocycles including sixteen 2-hydroxyisoquinoline-1,3(2H,4H)-dione derivatives for anti-HBV RNaseH activity. Nine compounds inhibited the HBV RNaseH, but activity was marginal for eight of them. Compound #1 [2-hydroxyisoquinoline-1,3(2H,4H)-dione, HID] was the best hit with an IC50 of 28.1μM and an EC50 of 4.2μM. It preferentially suppressed accumulation of the viral plus-polarity DNA strand in replication inhibition assays, indicating that replication was blocked due to suppression of HBV RNaseH activity. It had a CC50 of 75μM, yielding a therapeutic index of ∼18. The EC50 value was 7-fold lower than the IC50, possibly due to cellular retention or metabolism of the compound, or higher affinity for the full-length enzyme than the recombinant form used for screening. These data indicate that the 2-hydroxyisoquinoline-1,3(2H,4H)-diones will have different structure-activity relationships for the HBV and HIV RNaseHs. Therefore, HID compounds may provide a foundation for development of more effective RNaseH inhibitors of HBV replication.
Keywords: 2-Hydroxyisoquinoline-13(2H,4H)-diones; Hepatitis B virus; Ribonuclease H; Viral replication.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The hepatitis B virus ribonuclease H is sensitive to inhibitors of the human immunodeficiency virus ribonuclease H and integrase enzymes.PLoS Pathog. 2013 Jan;9(1):e1003125. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003125. Epub 2013 Jan 22. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 23349632 Free PMC article.
-
β-Thujaplicinol inhibits hepatitis B virus replication by blocking the viral ribonuclease H activity.Antiviral Res. 2013 Sep;99(3):221-9. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.06.007. Epub 2013 Jun 21. Antiviral Res. 2013. PMID: 23796982
-
Inhibition of HBV replication by N-hydroxyisoquinolinedione and N-hydroxypyridinedione ribonuclease H inhibitors.Antiviral Res. 2019 Apr;164:70-80. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2019.02.005. Epub 2019 Feb 12. Antiviral Res. 2019. PMID: 30768944 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical Approaches to Inhibiting the Hepatitis B Virus Ribonuclease H.ACS Infect Dis. 2019 May 10;5(5):655-658. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.8b00045. Epub 2018 Mar 22. ACS Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 29565562 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The hepatitis B virus ribonuclease H as a drug target.Antiviral Res. 2015 Jun;118:132-8. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2015.04.002. Epub 2015 Apr 8. Antiviral Res. 2015. PMID: 25862291 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
3-Hydroxypyrimidine-2,4-Diones as Novel Hepatitis B Virus Antivirals Targeting the Viral Ribonuclease H.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017 May 24;61(6):e00245-17. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00245-17. Print 2017 Jun. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017. PMID: 28320718 Free PMC article.
-
3,7-Dihydroxytropolones Inhibit Initiation of Hepatitis B Virus Minus-Strand DNA Synthesis.Molecules. 2020 Sep 27;25(19):4434. doi: 10.3390/molecules25194434. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32992516 Free PMC article.
-
The current status and future directions of hepatitis B antiviral drug discovery.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2017 Jan;12(1):5-15. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2017.1255195. Epub 2016 Nov 11. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2017. PMID: 27797587 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Therapies for Chronic Hepatitis B and the Potential for a Functional Cure.Drugs. 2023 Apr;83(5):367-388. doi: 10.1007/s40265-023-01843-2. Epub 2023 Mar 11. Drugs. 2023. PMID: 36906663
-
Unveiling the roles of HBV polymerase for new antiviral strategies.Future Virol. 2015;10(3):283-295. doi: 10.2217/fvl.14.113. Future Virol. 2015. PMID: 25893003 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Billamboz M, Bailly F, Barreca ML, De LL, Mouscadet JF, Calmels C, Andreola ML, Witvrouw M, Christ F, Debyser Z, Cotelle P. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of a series of 2-hydroxyisoquinoline-1,3(2H,4H)-diones as dual inhibitors of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integrase and the reverse transcriptase RNase H domain. J.Med.Chem. 2008;51:7717–7730. - PubMed
-
- Billamboz M, Bailly F, Lion C, Calmels C, Andreola ML, Witvrouw M, Christ F, Debyser Z, De Luca L, Chimirri A, Cotelle P. 2-hydroxyisoquinoline-1,3(2H,4H)-diones as inhibitors of HIV-1 integrase and reverse transcriptase RNase H domain: influence of the alkylation of position 4. European journal of medicinal chemistry. 2011a;46:535–546. - PubMed
-
- Billamboz M, Bailly F, Lion C, Touati N, Vezin H, Calmels C, Andreola ML, Christ F, Debyser Z, Cotelle P. Magnesium chelating 2-hydroxyisoquinoline-1,3(2H,4H)-diones, as inhibitors of HIV-1 integrase and/or the HIV-1 reverse transcriptase ribonuclease H domain: discovery of a novel selective inhibitor of the ribonuclease H function. J.Med.Chem. 2011b;54:1812–1824. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

