Estrogen regulation of the brain renin-angiotensin system in protection against angiotensin II-induced sensitization of hypertension
- PMID: 24858844
- PMCID: PMC4101642
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.01012.2013
Estrogen regulation of the brain renin-angiotensin system in protection against angiotensin II-induced sensitization of hypertension
Abstract
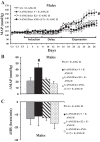
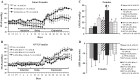
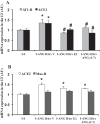
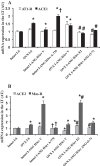
This study investigated sex differences in the sensitization of angiotensin (ANG) II-induced hypertension and the role of central estrogen and ANG-(1-7) in this process. Male and female rats were implanted for telemetered blood pressure (BP) recording. A subcutaneous subpressor dose of ANG II was given alone or concurrently with intracerebroventricular estrogen, ANG-(1-7), an ANG-(1-7) receptor antagonist A-779 or vehicle for 1 wk (induction). After a 1-wk rest (delay), a pressor dose of ANG II was given for 2 wk (expression). In males and ovariectomized females, subpressor ANG II had no sustained effect on BP during induction, but produced an enhanced hypertensive response to the subsequent pressor dose of ANG II during expression. Central administration of estrogen or ANG-(1-7) during induction blocked ANG II-induced sensitization. In intact females, subpressor ANG II treatment produced a decrease in BP during induction and delay, and subsequent pressor ANG II treatment given during expression produced only a slight but significant increase in BP. However, central blockade of ANG-(1-7) by intracerebroventricular infusion of A-779 during induction restored the decreased BP observed in females during induction and enhanced the pressor response to the ANG II treatment during expression. RT-PCR analyses indicated that estrogen given during induction upregulated mRNA expression of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) antihypertensive components, whereas both central estrogen and ANG-(1-7) downregulated mRNA expression of RAS hypertensive components in the lamina terminalis. The results indicate that females are protected from ANG II-induced sensitization through central estrogen and its regulation of brain RAS.
Keywords: angiotensin II; angiotensin-(1–7), central nervous system; blood pressure; sex difference.
Copyright © 2014 the American Physiological Society.
Figures
References
-
- Brosnihan KB, Neves LA, Joyner J, Averill DB, Chappell MC, Sarao R, Penninger J, Ferrario CM. Enhanced renal immunocytochemical expression of ANG-(1–7) and ACE2 during pregnancy. Hypertension 42: 749–753, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Brown RD, Hilliard LM, Head GA, Jones ES, Widdop RE, Denton KM. Sex differences in the pressor and tubuloglomerular feedback response to angiotensin II. Hypertension 59: 129–135, 2012 - PubMed
-
- Carroll ME, Anker JJ. Sex differences and ovarian hormones in animal models of drug dependence. Horm Behav 58: 44–56, 2010 - PubMed
-
- Cerrato BD, Frasch AP, Nakagawa P, Longo-Carbajosa N, Peña C, Höcht C, Gironacci MM. Angiotensin-(1–7) upregulates central nitric oxide synthase in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Brain Res 1453: 1–7, 2012 - PubMed
-
- Chappell MC, Pirro NT, Sykes A, Ferrario CM. Metabolism of angiotensin-(1–7) by angiotensin converting enzyme. Hypertension 31: 362–367, 1998 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

