Surgical management of functional bladder outlet obstruction in adults with neurogenic bladder dysfunction
- PMID: 24859260
- PMCID: PMC11162557
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004927.pub4
Surgical management of functional bladder outlet obstruction in adults with neurogenic bladder dysfunction
Abstract
Background: The most common type of functional bladder outlet obstruction in patients with neurogenic bladder is detrusor-sphincter dyssynergia (DSD). The lack of co-ordination between the bladder and the external urethral sphincter muscle (EUS) in DSD can result in poor bladder emptying and high bladder pressures, which may eventually lead to progressive renal damage.
Objectives: To assess the effectiveness of different surgical therapies for the treatment of functional bladder outlet obstruction (i.e. DSD) in adults with neurogenic bladder dysfunction.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Incontinence Group Specialised Register, which contains trials identified from the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE, MEDLINE In-Process, and handsearching of journals and conference proceedings (searched 20 February 2014), and the reference lists of relevant articles.
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) or quasi-RCTs comparing a surgical treatment of DSD in adults suffering from neurogenic bladder dysfunction, with no treatment, placebo, non-surgical treatment, or other surgical treatment, alone or in combination.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently assessed trial quality and extracted data.
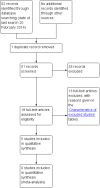
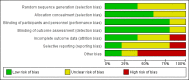
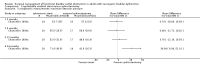
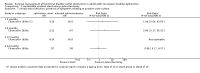
Main results: We included five trials (total of 199 participants, average age of 40 years). The neurological diseases causing DSD were traumatic spinal cord injury (SCI), multiple sclerosis (MS), or congenital malformations.One trial compared placement of sphincteric stent prosthesis with sphincterotomy. For urodynamic measurements, results for postvoid residual urine volume (PVR) and cystometric bladder capacity were inconclusive and consistent with benefit of either sphincteric stent prosthesis or sphincterotomy at three, six, 12, and 24 months. Results for maximum detrusor pressure (Pdet.max) were also inconclusive at three, six, and 12 months; however, after two years, the Pdet.max after sphincterotomy was lower than after stent placement (mean difference (MD) -30 cmH2O, 95% confidence interval (CI) 8.99 to 51.01).Four trials considered botulinum A toxin (BTX-A) injection in the EUS, either alone or in combination with other treatments. The comparators included oral baclofen, oral alpha blocker, lidocaine, and placebo. The BTX-A trials all differed in protocols, and therefore we did not undertake meta-analysis. A single 100 units transperineal BTX-A injection (Botox®) in patients with MS resulted in higher voided urine volumes (MD 69 mL, 95% CI 11.87 to 126.13), lower pre-micturition detrusor pressure (MD -10 cmH2O, 95% CI -17.62 to -2.38), and lower Pdet.max (MD -14 cmH2O, 95% CI -25.32 to -2.68) after 30 days, compared to placebo injection. Results for PVR using catheterisation, basal detrusor pressure, maximal bladder capacity, maximal urinary flow, bladder compliance at functional bladder capacity, maximal urethral pressure, and closure urethral pressure at 30 days were inconclusive and consistent with benefit of either BTX-A injection or placebo injections. In participants with SCI, treatment with 200 units of Chinese manufactured BTX-A injected at eight different sites resulted in better bladder compliance (MD 7.5 mL/cmH2O, 95% CI -10.74 to -4.26) than participants who received the same injections with the addition of oral baclofen. Results for maximum uroflow rate, maximal cystometric capacity, and volume per voiding were inconclusive and consistent with benefit of either BTX-A injection or BTX-A injection with the addition of oral baclofen. However, the poor quality of reporting in this trial caused us to question the relevance of bladder compliance as an adequate outcome measure.In participants with DSD due to traumatic SCI, MS, or congenital malformation, the results for PVRs after one day were inconclusive and consistent with benefit of either a single 100 units transperineal BTX-A (Botox®) injection or lidocaine injection. However, after seven and 30 days of BTX-A injection, PVRs were lower (MD -163 and -158 mL, 95% CI -308.65 to -17.35 and 95% CI -277.57 to -39.03, respectively) compared to participants who received lidocaine injections. Results at one month for Pdet.max on voiding, EUS activity in electromyography, and maximal urethral pressure were inconclusive and consistent with benefit of either BTX-A or lidocaine injections.Finally, one small trial consisting of five men with SCI compared weekly BTX-A injections with normal saline as placebo. The placebo had no effect on DSD in the two participants allocated to the placebo treatment. Their urodynamic parameters were unchanged from baseline values until subsequent injections with BTX-A once a week for three weeks. These subsequent injections resulted in similar responses to those of the three participants who were allocated to the BTX-A treatment. Unfortunately, the report presented no data on placebo treatment.Only the trial that compared sphincterotomy with stent placement reported outcome measures renal function and urologic complications related to DSD. Results for renal function at 12 and 24 months, and urologic complications related to DSD at three, six, 12, and 24 months were inconclusive and consistent with benefit of either sphincteric stent prosthesis or sphincterotomy.Adverse effects reported were haematuria due to the cystoscopic injection and muscle weakness, of which the latter may be related to the BTX-A dose used.All trials had some methodological shortcomings, so insufficient information was available to permit judgement of risk of bias. At least half of the trials had an unclear risk of selection bias and reporting bias. One trial had a high risk of attrition bias, and another trial had a high risk of reporting bias.
Authors' conclusions: Results from small studies with a high risk of bias have identified evidence of limited quality that intraurethral BTX-A injections improve some urodynamic measures after 30 days in the treatment of functional bladder outlet obstruction in adults with neurogenic bladder dysfunction. The necessity of reinjection of BTX-A is a significant drawback; a sphincterotomy might therefore be a more effective treatment option for lowering bladder pressure in the long-term.However, because of the limited availability of eligible trials, this review was unable to provide robust evidence in favour of any of the surgical treatment options. More RCTs are needed, measuring improvement on quality of life, and on other types of surgical treatment options for DSD since these are lacking. Future RCTs assessing the effectiveness of BTX-A injections also need to address the uncertainty about the optimal dose and mode of injection for this specific type of urological condition.
Conflict of interest statement
Elaine Utomo: none stated. Jan Groen: none stated. Bertil FM Blok: none stated.
Figures













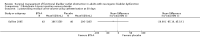



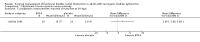













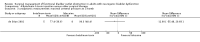





Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004927.pub3
References
References to studies included in this review
Chancellor 1999a {published data only}
-
- Chancellor MB, Bennett C, Simoneau AR, Finocchiaro MV, Kline C, Bennett JK, et al. Sphincteric stent versus external sphincterotomy in spinal cord injured men: prospective randomized multicenter trial. Journal of Urology 1999;161(6):1893‐8. [PUBMED: 10332461] - PubMed
Cui 2007 {published data only}
-
- Cui X‐G, Qu C‐Y, Xu D‐F, Ren J‐Z, Kong L‐L, Lin H‐Y. Botulinum toxin injection into urethral external sphincter combined with oral baclofen in treatment of patients with detrusor‐external sphincter dyssynergia after spinal cord injury. Academic Journal of Second Military Medical University 2007;28(8):875‐7.
de Sèze 2002 {published data only}
-
- Sèze M, Petit H, Gallien P, Sèze MP, Joseph PA, Mazaux JM, et al. Botulinum A toxin and detrusor sphincter dyssynergia: a double‐blind lidocaine‐controlled study in 13 patients with spinal cord disease. European Urology 2002;42(1):56‐62. [PUBMED: 12121731] - PubMed
Dykstra 1990 {published data only}
-
- Dykstra DD, Sidi AA. Treatment of detrusor‐sphincter dyssynergia with botulinum A toxin: a double‐blind study. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 1990;71(1):24‐6. [PUBMED: 2297305] - PubMed
Gallien 2005 {published data only}
-
- Gallien P, Reymann JM, Amarenco G, Nicolas B, Sèze M, Bellissant E. Placebo controlled, randomised, double blind study of the effects of botulinum A toxin on detrusor sphincter dyssynergia in multiple sclerosis patients. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 2005;76(12):1670‐6. [PUBMED: 16291892] - PMC - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Chancellor 1994a {published data only}
-
- Chancellor MB, Rivas DA, Abdill CK, Karasick S, Ehrlich SM, Staas WE. Prospective comparison of external sphincter balloon dilatation and prosthesis placement with external sphincterotomy in spinal cord injured men. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 1994;75:297‐305. [PUBMED: 8129583] - PubMed
Dunn 2000 {published data only}
-
- Dunn MD, Portis AJ, Kahn SA Yan Y, Shalhav AL, Elbahnasy AM, et al. Clinical effectiveness of new stent design: randomized single‐blind comparison of tail and double‐pigtail stents. Journal of Endourology 2000;14(2):195‐202. [PUBMED: 10772515] - PubMed
Herschorn 2009 {published data only}
-
- Herschorn S, Gajewski J, Ethans K, Corcos J, Carlson K, Bailly G, et al. Efficacy of botulinum toxin A injection for neurogenic detrusor overactivity and urinary incontinence ‐ a randomized double‐blind trial (Abstract number 33). Neurourology and Urodynamics 2009;28(7):608‐9. - PubMed
Herschorn 2009a {published data only}
-
- Herschorn S, Gajewski J, Ethans K, Corcos J, Carlson K, Bailly G, et al. Botulinum toxin A in patients with neurogenic detrusor overactivity: preliminary results from a Canadian multicentre randomized trial (Abstract number: Poster# 50). Neurourology and Urodynamics 2009;28(2):138‐9.
Loubser 1991 {published data only}
-
- Loubser PG, Narayan RK, Sandin KJ, Donovan WH, Russell KD. Continuous infusion of intrathecal baclofen: long‐term effects on spasticity in spinal cord injury. Paraplegia 1991;29(1):48‐64. [PUBMED: 2023770] - PubMed
Mehta 2012 {published data only}
-
- Mehta S, Hill D, Foley N, Hsieh J, Ethans K, Potter P, et al. A meta‐analysis of botulinum toxin sphincteric injections in the treatment of incomplete voiding after spinal cord injury. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2012;93(4):597‐603. [PUBMED: 22365478] - PubMed
Meythaler 2001 {published data only}
-
- Meythaler JM Guin‐Renfroe S Brunner RC Hadley MN. Intrathecal baclofen for spastic hypertonia from stroke. Stroke 2001;32(9):2099‐109. [PUBMED: 11546903] - PubMed
Naumann 2008 {published data only}
-
- Naumann M, So Y, Argoff CE, Childers MK, Dykstra DD, Gronseth GS, et al. Assessment: Botulinum neurotoxin in the treatment of autonomic disorders and pain (an evidence‐based review): report of the Therapeutics and Technology Assessment Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2008;70(19):1707‐14. [PUBMED: 18458231] - PubMed
Schurch 2004a {published data only}
-
- Schurch B, Seze M, Denys P, Chartier‐Kastler E, Ismael S, Haab F, et al. Botulinum toxin A (Botox) in neurogenic urinary incontinence: results from a multi‐centre randomised, controlled trial (Abstract). Neurourology and Urodynamics. 2004; Vol. 23, issue 5/6:609‐10.
Schurch 2005a {published data only}
-
- Schurch B, Sèze M, Denys P, Chartier‐Kastler E, Haab F, Everaert K, et al. Subgroup analysis to determine impact of patient demographics on urodynamic response to focal administration of botulinum toxin A (Abstract). Neurourology and Urodynamics 2005;24(5/6):545‐6.
Schurch 2007 {published data only}
-
- Schurch B, Denys P, Kozma CM, Reese PR, Slaton T, Barron RL. Botulinum toxin a improves the quality of life of patients with neurogenic urinary incontinence. European Urology 2007;52(3):850‐8. [PUBMED: 17467889] - PubMed
Steers 1992 {published data only}
-
- Steers WD, Meythaler JM, Haworth C, Herrell D, Park TS. Effects of acute bolus and chronic continuous intrathecal baclofen on genitourinary dysfunction due to spinal cord pathology. Journal of Urology 1992;148(6):1849‐55. [PUBMED: 1433619] - PubMed
Thavaseelan 2005 {published data only}
-
- Thavaseelan JT, Burns‐Cox N, Jordan K, Trewhella J. Efficacy of botulinum toxin type A (BOTOX) in the management of the neurogenic bladder: a prospective, randomised, double blind, dose comparative trial ‐ interim overview of results (Abstract). BJU International 2005;95(Suppl 1):4‐5.
Additional references
Abdul‐Rahman 2010
-
- Abdul‐Rahman A, Ismail S, Hamid R, Shah J. A 20‐year follow‐up of the mesh wallstent in the treatment of detrusor external sphincter dyssynergia in patients with spinal cord injury. BJU International 2010;106(10):1510‐3. [PUBMED: 20500511] - PubMed
Abrams 2002
-
- Abrams P, Cardozo L, Fall M, Griffiths D, Rosier P, Ulmsten U, et al. The standardisation of terminology of lower urinary tract function: Report from the standardisation sub‐committee of the international continence society. Neurourology and Urodynamics 2002;21(2):167‐78. [DOI: 10.1002/nau.10052] - DOI - PubMed
Angaut‐Petit 1990
-
- Angaut‐Petit D, Molgó J, Comella JX, Faille L, Tabti N. Terminal sprouting in mouse neuromuscular junctions poisoned with botulinum type A toxin: morphological and electrophysiological features. Neuroscience 1990;37(3):799‐808. [PUBMED: 1701041] - PubMed
Araki 2003
-
- Araki I, Matsui M, Ozawa K, Takeda M, Kuno S. Relationship of bladder dysfunction to lesion site in multiple sclerosis. Journal of Urology 2003;169(4):1384‐7. [PUBMED: 12629367] - PubMed
Barry 1992
-
- Barry MJ, Fowler FJ Jr, O'Leary MP, Bruskewitz RC, Holtgrewe L, Mebust WK, et al. The American Urological Association symptom index for benign prostatic hyperplasia. The Measurement Committee of the American Urological Association. Journal of Urology 1992;148(5):1549‐57. [PUBMED: 1279218] - PubMed
Blaivas 1981
-
- Blaivas JG, Sinha HP, Zayed AA, Labib KB. Detrusor‐external sphincter dyssynergia: a detailed electromyographic study. Journal of Urology 1981;125(4):545‐8. [PUBMED: 7218457] - PubMed
Blok 1997
-
- Blok BF, de Weerd H, Holstege G. The pontine micturition center projects to sacral cord GABA immunoreactive neurons in the cat. Neuroscience Letters 1997;233(2‐3):109‐12. [PUBMED: 9350844] - PubMed
Blok 2002
-
- Blok BF. Central pathways controlling micturition and urinary continence. Urology 2002;59(5 Suppl 1):13‐7. [PUBMED: 12007517] - PubMed
Boger 2008
-
- Boger A, Bhadra N, Gustafson KJ. Bladder voiding by combined high frequency electrical pudendal nerve block and sacral root stimulation. Neurourology and Urodynamics 2008;27(5):435‐9. [PUBMED: 18041769] - PubMed
Brooks 1996
-
- Brooks R. EuroQol: the current state of play. Health Policy 1996;37(1):53‐72. [PUBMED: 10158943] - PubMed
Cameron 2010
-
- Cameron AP, Wallner LP, Tate DG, Sarma AV, Rodriguez GM, Clemens JQ. Bladder management after spinal cord injury in the United States 1972 to 2005. Journal of Urology 2010;184(1):213‐7. [PUBMED: 20478597] - PubMed
Chancellor 1992
-
- Chancellor MB, Hirsch IH, Kiilholma P, Staas WE. Technique of external sphincter balloon dilatation. Urology 1992;40(4):308‐10. [PUBMED: 1413347] - PubMed
Chancellor 1993
-
- Chancellor MB, Karasick S, Strup S, Abdill CK, Hirsch IH, Staas WE. Transurethral balloon dilation of the external urinary sphincter: effectiveness in spinal cord‐injured men with detrusor‐external urethral sphincter dyssynergia. Radiology 1993;187(2):557‐60. [PUBMED: 8475307] - PubMed
Chancellor 1994
-
- Chancellor MB, Rivas DA, Abdill CK, Karasick S, Ehrlich SM, Staas WE. Prospective comparison of external sphincter balloon dilatation and prosthesis placement with external sphincterotomy in spinal cord injured men. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilation 1994;75(3):297‐305. [PUBMED: 8129583] - PubMed
Chancellor 1999b
-
- Chancellor MB, Gajewski J, Ackman CF, Appell RA, Bennett J, Binard J, et al. Long‐term followup of the North American multicenter UroLume trial for the treatment of external detrusor‐sphincter dyssynergia. Journal of Urology 1999;161(5):1545‐50. [PUBMED: 10210393] - PubMed
Costa 2001
-
- Costa P, Perrouin‐Verbe B, Colvez A, Didier J, Marquis P, Marrel A, et al. Quality of life in spinal cord injury patients with urinary difficulties. Development and validation of qualiveen. European Urology 2001;39(1):107‐13. [PUBMED: 11173948] - PubMed
Dykstra 1988
-
- Dykstra DD, Sidi AA, Scott AB, Pagel JM, Goldfish GD. Effects of botulinum A toxin on detrusor‐sphincter dyssynergia in spinal cord injury patients. Journal of Urology 1988;139(5):919‐22. [PUBMED: 3361663] - PubMed
EROS 2013 [Computer program]
-
- Institute of Clinical Effectiveness and Health Policy. Early Review Organizing Software (EROS). Buenos Aires, Argentina: Institute of Clinical Effectiveness and Health Policy, 2013. [http://www.eros‐systematic‐review.org/]
Feifer 2008
-
- Feifer A, Corcos J. Contemporary role of suprapubic cystostomy in treatment of neuropathic bladder dysfunction in spinal cord injured patients. Neurourology and Urodynamics 2008;27(6):475‐9. [PUBMED: 18551568] - PubMed
Ganesan 2001
-
- Ganesan V, Borzyskowski M. Characteristics and course of urinary tract dysfunction after acute transverse myelitis in childhood. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology 2001;43(7):473‐5. [PUBMED: 11463178] - PubMed
Gaunt 2009
-
- Gaunt RA, Prochazka A. Transcutaneously coupled, high‐frequency electrical stimulation of the pudendal nerve blocks external urethral sphincter contractions. Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair 2009;23(6):615‐26. [PUBMED: 19109445] - PubMed
Gross 2009
-
- Gross RA, Johnston KC. Levels of evidence: Taking Neurology to the next level. Neurology 2009;72(1):8‐10. [PUBMED: 19122025] - PubMed
Hagen 2010
Hamid 2003
-
- Hamid R, Arya M, Wood S, Patel HRH, Shah PJR. The use of the Memokath stent in the treatment of detrusor sphincter dyssynergia in spinal cord injury patients: a single‐center seven‐year experience. European Urology 2003;43:539‐43. [PUBMED: 12706000] - PubMed
Hansen 2004
-
- Hansen RB, Biering‐Sorensen F, Kristensen JK. Bladder emptying over a period of 10‐45 years after a traumatic spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 2004;42:631‐7. [PUBMED: 15326470] - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org 2011.
Hoffman 2000
Hoffman 2012
Jamison 2004
Kalisvaart 2010
-
- Kalisvaart JF, Katsumi HK, Ronningen LD, Hovey RM. Bladder cancer in spinal cord injury patients. Spinal Cord 2010;48(3):257‐61. [PUBMED: 19752870] - PubMed
Kalita 2002
Kirkham 2010
Ko 1997
-
- Ko HY, Kim KT. Treatment of external urethral sphincter hypertonicity by pudendal nerve block using phenol solution in patients with spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 1997;35(10):690‐3. [PUBMED: 9347599] - PubMed
Liu 2010
-
- Liu CW, Attar KH, Gall A, Shah J, Craggs M. The relationship between bladder management and health‐related quality of life in patients with spinal cord injury in the UK. Spinal Cord 2010;48(4):319‐24. [PUBMED: 19841636] - PubMed
Madhuvrata 2012
McFarlane 1997
-
- McFarlane JP, Foley SJ, Shah PJ. Balloon dilatation of the external urethral sphincter in the treatment of detrusor‐sphincter dyssynergia. Spinal Cord 1997;35(2):96‐8. [PUBMED: 9044516] - PubMed
Milroy 1988
-
- Milroy EJ, Chapple CR, Cooper JE, Eldin A, Wallsten H, Seddon AM, et al. A new treatment for urethral strictures. Lancet 1988;1(8600):1424‐7. [PUBMED: 2898583] - PubMed
Miyazato 2008
-
- Miyazato M, Sasatomi K, Hiragata S, Sugaya K, Chancellor MB, Groat WC, et al. Suppression of detrusor‐sphincter dyssynergia by GABA‐receptor activation in the lumbosacral spinal cord in spinal cord‐injured rats. American Journal of Physiology. Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology 2008;295(1):R336‐42. [PUBMED: 18495826] - PMC - PubMed
Moher 2010
Moore 2009
Nabi 2009
-
- Nabi G, Cody JD, Dublin N, McClinton S, N'Dow JMO, Neal DE, et al. Urinary diversion and bladder reconstruction/replacement using intestinal segments for intractable incontinence or following cystectomy. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2009, Issue 1. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003306] - DOI
Ord 2003
-
- Ord J, Lunn D, Reynard J. Bladder management and risk of bladder stone formation in spinal cord injured patients. Journal of Urology 2003;170(5):1734‐7. [PUBMED: 14532765] - PubMed
Pan 2009
-
- Pan D, Troy A, Rogerson J, Bolton D, Brown D, Lawrentschuk N. Long‐term outcomes of external sphincterotomy in a spinal injured population. Journal of Urology 2009;181(2):705‐9. [PUBMED: 19091341] - PubMed
Pannek 2011
-
- Pannek J, Stöhrer M, Blok B, Castro‐Diaz D, Popolo G, Kramer G, et al. Guidelines on Neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction. EAU Guidelines, edition presented at the 25th EAU Annual Congress, Barcelona. Arnhem, the Netherlands: EAU Guidelines Office, 2011.
Perkash 1976
-
- Perkash I. Modified approach to sphincterotomy in spinal cord injury patients. Indications, technique and results in 32 patients. Paraplegia 1976;13(4):247‐60. [PUBMED: 1264480] - PubMed
Perkash 1998
-
- Perkash I. Use of contact laser crystal tip firing Nd:YAG to relieve urinary outflow obstruction in male neurogenic bladder patients. Journal of Clinical Laser Medicine & Surgery 1998;16(1):33‐8. [PUBMED: 9728128] - PubMed
Reference Manager 2012 [Computer program]
-
- New York: Thomson Reuters. Reference Manager Professional Edition. Version 12. New York: Thomson Reuters, 2012.
Reynard 2003
-
- Reynard JM, Vass J, Sullivan ME, Mamas M. Sphincterotomy and the treatment of detrusor‐sphincter dyssynergia: current status, future prospects. Spinal Cord 2003;41(1):1‐11. [PUBMED: 12494314] - PubMed
Rivas 1995
-
- Rivas DA, Chancellor MB, Staas WE Jr, Gomella LG. Contact neodymium: yttrium‐aluminium‐garnet laser ablation of the external sphincter in spinal cord injured men with detrusor sphincter dyssynergia. Urology 1995;45(6):1028‐31. [PUBMED: 7771003] - PubMed
Ross 1987
Sahai 2005
-
- Sahai A, Khan M, Fowler CJ, Dasgupta P. Botulinum toxin for the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms: a review. Neurourology and Urodynamics 2005;24(1):2‐12. [PUBMED: 15578628] - PubMed
Satoh 1979
-
- Satoh Y, Sakurai T, Ikoma F. A treatment of detrusor‐sphincter dyssynergia: pudendal nerve block by phenolglycerin under the guide of direct nerve stimulation. Der Urologe A 1979;18(5):284‐8. [PUBMED: 494454] - PubMed
Schurch 1996
-
- Schurch B, Hauri D, Rodic B, Curt A, Meyer M, Rossier AB. Botulinum‐A toxin as a treatment of detrusor‐sphincter dyssynergia: a prospective study in 24 spinal cord injury patients. Journal of Urology 1996;155(3):1023‐9. [PUBMED: 8583552] - PubMed
Shaw 1990
-
- Shaw PJ, Milroy EJ, Timoney AG, Din A, Mitchell N. Permanent external striated sphincter stents in patients with spinal injuries. British Journal of Urology 1990;66(3):297‐302. [PUBMED: 2207546] - PubMed
Shumaker 1994
-
- Shumaker SA, Wyman JF, Uebersax JS, McClish D, Fantl JA. Health‐related quality of life measures for women with urinary incontinence: the Incontinence Impact Questionnaire and the Urogenital Distress Inventory. Continence Program in Women (CPW) Research Group. Quality of Life Research 1994;3(5):291‐306. [DOI: 10.1007/BF00451721; PUBMED: 7841963] - DOI - PubMed
Simon 2010
-
- Simon O, Yelnik AP. Managing spasticity with drugs. European Journal of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine 2010;46(3):401‐10. [PUBMED: 20927006] - PubMed
Soni 1994
-
- Soni BM, Vaidyanatham S, Krishnan KR. Use of Memokath, a second generation urethral stent for relief of urinary retention in male spinal cord injured patients. Paraplegia 1994;32(7):480‐8. [PUBMED: 7970850] - PubMed
Stöhrer 2009
-
- Stöhrer M, Blok B, Castro‐Diaz D, Chartier‐Kastler E, Del Popolo G, Kramer G, et al. EAU guidelines on neurogenic lower urinary tract dysfunction. European Urology 2009;56(1):81‐8. [PUBMED: 19403235] - PubMed
Tai 2004
-
- Tai C, Roppolo JR, Groat WC. Block of external urethral sphincter contraction by high frequency electrical stimulation of pudendal nerve. Journal of Urology 2004;172(5 Pt 1):2069‐72. [PUBMED: 15540791] - PubMed
Tai 2005
-
- Tai C, Roppolo JR, Groat WC. Response of external urethral sphincter to high frequency biphasic electrical stimulation of pudendal nerve. Journal of Urology 2005;174(2):782‐6. [PUBMED: 16006976] - PubMed
Tsai 2002
-
- Tsai SJ, Lew HL, Date E, Bih LI. Treatment of detrusor‐sphincter dyssynergia by pudendal nerve block in patients with spinal cord injury. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2002;83(5):714‐7. [PUBMED: 11994813] - PubMed
Ukkonen 2004
-
- Ukkonen M, Elovaara I, Dastidar P, Tammela TL. Urodynamic findings in primary progressive multiple sclerosis are associated with increased volumes of plaques and atrophy in the central nervous system. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica 2004;109(2):100‐5. [PUBMED: 14705971] - PubMed
van Gool 2001
-
- Gool JD, Dik P, Jong TP. Bladder‐sphincter dysfunction in myelomeningocele. European Journal of Pediatrics 2001;160(7):414‐20. [PUBMED: 11475578] - PubMed
Ware 1992
-
- Ware JE Jr, Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36‐item short‐form health survey (SF‐36). I. Conceptual framework and item selection. Medical Care 1992;30(6):473‐83. [PUBMED: 1593914] - PubMed
Weld 2000
-
- Weld KJ, Graney MJ, Dmochowski RR. Clinical significance of detrusor sphincter dyssynergia type in patients with post‐traumatic spinal cord injury. Urology 2000;56(4):565‐8. [PUBMED: 11018603] - PubMed
Westgren 1998
-
- Westgren N, Levi R. Quality of life and traumatic spinal cord injury.. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 1998;79(11):1433‐9. [PUBMED: 9821906] - PubMed
Williamson 2011
Wong 2012
Wyndaele 2009
-
- Wyndaele JJ, Kovindha A, Madersbacher H, Radziszweski P, Ruffion A, Schurch B, et al. Neurologic urinary and faecal incontinence. In: Abrams P, Cardozo L, Khoury S, Wein A editor(s). Incontinence. 4th Edition. Health Publication Ltd, 2009:793‐960.
Yalcin 2003
-
- Yalcin I, Bump RC. Validation of two global impression questionnaires for incontinence. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2003;189(1):98‐101. [PUBMED: 12861145] - PubMed
Yalla 1977
-
- Yalla SV, Blunt KJ, Fam BA, Constantinople NL, Gittes RF. Detrusor‐urethral sphincter dyssynergia. Journal of Urology 1977;118(6):1026‐9. [PUBMED: 926242] - PubMed
Zigmond 1983
-
- Zigmond AS, Snaith RP. The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1983;67(6):361‐70. [PUBMED: 6880820] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

