Targeting histone lysine demethylases - progress, challenges, and the future
- PMID: 24859458
- PMCID: PMC4316176
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.05.009
Targeting histone lysine demethylases - progress, challenges, and the future
Abstract
N-Methylation of lysine and arginine residues has emerged as a major mechanism of transcriptional regulation in eukaryotes. In humans, N(ε)-methyllysine residue demethylation is catalysed by two distinct subfamilies of demethylases (KDMs), the flavin-dependent KDM1 subfamily and the 2-oxoglutarate- (2OG) dependent JmjC subfamily, which both employ oxidative mechanisms. Modulation of histone methylation status is proposed to be important in epigenetic regulation and has substantial medicinal potential for the treatment of diseases including cancer and genetic disorders. This article provides an introduction to the enzymology of the KDMs and the therapeutic possibilities and challenges associated with targeting them, followed by a review of reported KDM inhibitors and their mechanisms of action from kinetic and structural perspectives.
Keywords: Demethylase; Epigenetics; Histone; Inhibition; Lysine; Methylation.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures





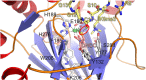

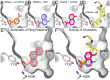

References
-
- Berdasco M., Esteller M. Aberrant epigenetic landscape in cancer: how cellular identity goes awry. Dev. Cell. 2010;19:698–711. - PubMed
-
- Suganuma T., Workman J.L. Signals and combinatorial functions of histone modifications. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2011;80:473–499. - PubMed
-
- Zentner G.E., Henikoff S. Regulation of nucleosome dynamics by histone modifications. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013;20:259–266. - PubMed
-
- Portela A., Esteller M. Epigenetic modifications and human disease. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010;28:1057–1068. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

