Structure and semi-sequence-specific RNA binding of Nrd1
- PMID: 24860164
- PMCID: PMC4081072
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gku446
Structure and semi-sequence-specific RNA binding of Nrd1
Abstract
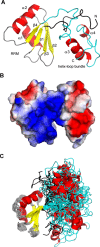
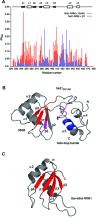
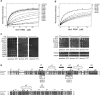
In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the Nrd1-dependent termination and processing pathways play an important role in surveillance and processing of non-coding ribonucleic acids (RNAs). The termination and subsequent processing is dependent on the Nrd1 complex consisting of two RNA-binding proteins Nrd1 and Nab3 and Sen1 helicase. It is established that Nrd1 and Nab3 cooperatively recognize specific termination elements within nascent RNA, GUA[A/G] and UCUU[G], respectively. Interestingly, some transcripts do not require GUA[A/G] motif for transcription termination in vivo and binding in vitro, suggesting the existence of alternative Nrd1-binding motifs. Here we studied the structure and RNA-binding properties of Nrd1 using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), fluorescence anisotropy and phenotypic analyses in vivo. We determined the solution structure of a two-domain RNA-binding fragment of Nrd1, formed by an RNA-recognition motif and helix-loop bundle. NMR and fluorescence data show that not only GUA[A/G] but also several other G-rich and AU-rich motifs are able to bind Nrd1 with affinity in a low micromolar range. The broad substrate specificity is achieved by adaptable interaction surfaces of the RNA-recognition motif and helix-loop bundle domains that sandwich the RNA substrates. Our findings have implication for the role of Nrd1 in termination and processing of many non-coding RNAs arising from bidirectional pervasive transcription.
© The Author(s) 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
References
-
- Bentley D. The mRNA assembly line: transcription and processing machines in the same factory. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2002;14:336–342. - PubMed
-
- Steinmetz E.J., Conrad N.K., Brow D.A., Corden J.L. RNA-binding protein Nrd1 directs poly(A)-independent 3′-end formation of RNA polymerase II transcripts. Nature. 2001;413:327–331. - PubMed
-
- Arigo J.T., Eyler D.E., Carroll K.L., Corden J.L. Termination of cryptic unstable transcripts is directed by yeast RNA-binding proteins Nrd1 and Nab3. Mol. Cell. 2006;23:841–851. - PubMed
-
- Thiebaut M., Kisseleva-Romanova E., Rougemaille M., Boulay J., Libri D. Transcription termination and nuclear degradation of cryptic unstable transcripts: a role for the nrd1-nab3 pathway in genome surveillance. Mol. Cell. 2006;23:853–864. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

