Native store-operated calcium channels are functionally expressed in mouse spinal cord dorsal horn neurons and regulate resting calcium homeostasis
- PMID: 24860175
- PMCID: PMC4229342
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2014.275065
Native store-operated calcium channels are functionally expressed in mouse spinal cord dorsal horn neurons and regulate resting calcium homeostasis
Abstract
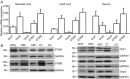
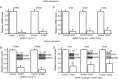
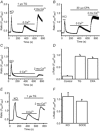
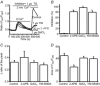
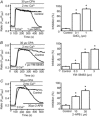
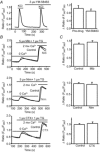
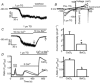
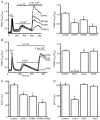
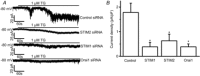
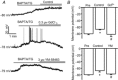
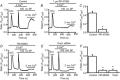
Store-operated calcium channels (SOCs) are calcium-selective cation channels that mediate calcium entry in many different cell types. Store-operated calcium entry (SOCE) is involved in various cellular functions. Increasing evidence suggests that impairment of SOCE is responsible for numerous disorders. A previous study demonstrated that YM-58483, a potent SOC inhibitor, strongly attenuates chronic pain by systemic or intrathecal injection and completely blocks the second phase of formalin-induced spontaneous nocifensive behaviour, suggesting a potential role of SOCs in central sensitization. However, the expression of SOCs, their molecular identity and function in spinal cord dorsal horn neurons remain elusive. Here, we demonstrate that SOCs are expressed in dorsal horn neurons. Depletion of calcium stores from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) induced large sustained calcium entry, which was blocked by SOC inhibitors, but not by voltage-gated calcium channel blockers. Depletion of ER calcium stores activated inward calcium-selective currents, which was reduced by replacing Ca(2+) with Ba(2+) and reversed by SOC inhibitors. Using the small inhibitory RNA knockdown approach, we identified both STIM1 and STIM2 as important mediators of SOCE and SOC current, and Orai1 as a key component of the Ca(2+) release-activated Ca(2+) channels in dorsal horn neurons. Knockdown of STIM1, STIM2 or Orai1 decreased resting Ca(2+) levels. We also found that activation of neurokinin 1 receptors led to SOCE and activation of SOCs produced an excitatory action in dorsal horn neurons. Our findings reveal that a novel SOC signal is present in dorsal horn neurons and may play an important role in pain transmission.
© 2014 The Authors. The Journal of Physiology © 2014 The Physiological Society.
Figures
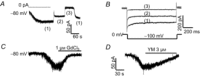

References
-
- Bakowski D. Parekh AB. Voltage-dependent Ba2+ permeation through store-operated CRAC channels: implications for channel selectivity. Cell Calcium. 2007;42:333–339. - PubMed
-
- Berna-Erro A, Braun A, Kraft R, Kleinschnitz C, Schuhmann MK, Stegner D, Wultsch T, Eilers J, Meuth SG, Stoll G. Nieswandt B. STIM2 regulates capacitive Ca2+ entry in neurons and plays a key role in hypoxic neuronal cell death. Sci Signal. 2009;2:ra67. - PubMed
-
- Bezprozvanny I. Hayden MR. Deranged neuronal calcium signaling and Huntington disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;322:1310–1317. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

