The effects of distraction on metacognition and metacognition on distraction: evidence from recognition memory
- PMID: 24860543
- PMCID: PMC4030143
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00439
The effects of distraction on metacognition and metacognition on distraction: evidence from recognition memory
Abstract
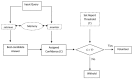
The effects of auditory distraction in memory tasks have, to date, been examined with procedures that minimize participants' control over their own memory processes. Surprisingly little attention has been paid to metacognitive control factors which might affect memory performance. In this study, we investigate the effects of auditory distraction on metacognitive control of memory, examining the effects of auditory distraction in recognition tasks utilizing the metacognitive framework of Koriat and Goldsmith (1996), to determine whether strategic regulation of memory accuracy is impacted by auditory distraction. Results replicated previous findings in showing that auditory distraction impairs memory performance in tasks minimizing participants' metacognitive control (forced-report test). However, the results revealed also that when metacognitive control is allowed (free-report tests), auditory distraction impacts upon a range of metacognitive indices. In the present study, auditory distraction undermined accuracy of metacognitive monitoring (resolution), reduced confidence in responses provided and, correspondingly, increased participants' propensity to withhold responses in free-report recognition. Crucially, changes in metacognitive processes were related to impairment in free-report recognition performance, as the use of the "don't know" option under distraction led to a reduction in the number of correct responses volunteered in free-report tests. Overall, the present results show how auditory distraction exerts its influence on memory performance via both memory and metamemory processes.
Keywords: auditory distraction; irrelevant speech; memory; metacognition; recognition.
Figures

References
-
- Beaman C. P. (2005a). Auditory distraction from low-intensity noise: a review of the consequences for learning and workplace environments. Appl. Cogn. Psychol. 19 1041–1064 10.1002/acp.1134 - DOI
-
- Beaman C. P. (2005b). Irrelevant sound effects amongst younger and older adults: objective findings and subjective insights. Eur. J. Cogn. Psychol. 17 241–265 10.1080/09541440440000023 - DOI
-
- Beaman C. P., Jones D. M. (1997). Role of serial order in the irrelevant speech effect: tests of the changing-state hypothesis. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 2 459–471 10.1037/0278-7393.23.2.459 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

