Accuracy of the VO2peak prediction equation in firefighters
- PMID: 24860611
- PMCID: PMC4016782
- DOI: 10.1186/1745-6673-9-17
Accuracy of the VO2peak prediction equation in firefighters
Abstract
Background: A leading contributing factor to firefighter injury and death is lack of fitness. Therefore, the Fire Service Joint Labor Management Wellness-Fitness Initiative (WFI) was established that includes a focus on providing fitness assessments to all fire service personnel. The current fitness assessment includes a submaximal exercise test protocol and associated prediction equation to predict individual VO2peak as a measure of fitness. There is limited information on the accuracy, precision, and sources of error of this prediction equation. This study replicated previous research by validating the accuracy of the WFI VO2peak prediction equation for a group of firefighters and further examining potential sources of error for an individual firefighters' assessment.
Methods: The sample consisted of 22 firefighters who completed a maximal exercise test protocol similar to the WFI submaximal protocol, but the test was terminated when firefighters reached a maximal level of exertion (i.e., measured VO2peak). We then calculated the predicted VO2peak based on the WFI prediction equation along with individual firefighters' body mass index (BMI) and 85% of maximum heart rate. The data were analyzed using paired samples t-tests in SPSS v. 21.0.
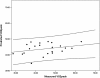
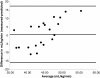
Results: The difference between predicted and measured VO2peak was -0.77 ± 8.35 mL•kg(-1)•min(-1). However, there was a weak, statistically non-significant association between measured VO2peak and predicted VO2peak (R(2) = 0.09, F(1,21) = 2.05, p = 0.17). The intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC = 0.215, p > 0.05) and Pearson (r = 0.31, p = 0.17) and Spearman (ρ = 0.28, p = 0.21) correlation coefficients were small. The standard error of the estimate (SEE) was 8.5 mL•kg(-1)•min(-1). Further, both age and baseline fitness level were associated with increased inaccuracy of the prediction equation.
Conclusions: We provide data on the inaccuracy and sources of error for the WFI VO2peak prediction equation for predicting fitness level in individual firefighters, despite apparently accurate predictions for a group of firefighters. These results suggest that the WFI prediction equation may need to be reevaluated as a means of precisely determining fitness for individual firefighters, which may affect employment status, duty assignment, and overall life safety of the firefighter.
Keywords: Aerobic capacity; Evaluation; Firefighter; Fitness; Validation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Validation of the firefighter WFI treadmill protocol for predicting VO2 max.Occup Med (Lond). 2015 Mar;65(2):143-6. doi: 10.1093/occmed/kqu189. Epub 2015 Jan 7. Occup Med (Lond). 2015. PMID: 25567508
-
Validation of a cardiorespiratory fitness assessment for firefighters.J Strength Cond Res. 2014 Oct;28(10):2717-23. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000000481. J Strength Cond Res. 2014. PMID: 24714540
-
Accuracy of peak VO2 assessments in career firefighters.J Occup Med Toxicol. 2011 Sep 25;6(1):25. doi: 10.1186/1745-6673-6-25. J Occup Med Toxicol. 2011. PMID: 21943154 Free PMC article.
-
Firefighter fitness: improving performance and preventing injuries and fatalities.Curr Sports Med Rep. 2011 May-Jun;10(3):167-72. doi: 10.1249/JSR.0b013e31821a9fec. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2011. PMID: 21623308 Review.
-
What do Firefighting Ability Tests Tell Us About Firefighter Physical Fitness? A Systematic Review of the Current Evidence.J Strength Cond Res. 2020 Jul;34(7):2093-2103. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000003577. J Strength Cond Res. 2020. PMID: 32287090
Cited by
-
Do police officers and firefighters have a higher risk of disease than other public officers? A 13-year nationwide cohort study in South Korea.BMJ Open. 2018 Jan 31;8(1):e019987. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-019987. BMJ Open. 2018. PMID: 29391373 Free PMC article.
-
Body Composition Is Related to Maximal Effort Treadmill Test Time in Firefighters.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 May 31;11(11):1607. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11111607. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37297747 Free PMC article.
-
A Submaximal Field Test of Aerobic Capacity does not Accurately Reflect VO2max in Career Firefighters.Int J Exerc Sci. 2022 Jan 1;15(4):221-230. doi: 10.70252/YLQD4760. eCollection 2022. Int J Exerc Sci. 2022. PMID: 36895840 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of peak oxygen consumption using cardiorespiratory parameters from warmup and submaximal stage of treadmill cardiopulmonary exercise test.PLoS One. 2024 Jan 10;19(1):e0291706. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0291706. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38198496 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation of Gerkin, Queen's College, George, and Jackson methods in estimating maximal oxygen consumption.Electron Physician. 2017 Oct 25;9(10):5525-5530. doi: 10.19082/5525. eCollection 2017 Oct. Electron Physician. 2017. PMID: 29238493 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Perroni F, Tessitore A, Cortis C, Lupo C, D’artibale E, Cignitti L, Capranica L. Energy cost and energy sources during a simulated firefighting activity. J Strength Cond Res. 2010;2(12):3457–3463. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

