Effect of single tablet of fixed-dose amlodipine and atorvastatin on blood pressure/lipid control, oxidative stress, and medication adherence in type 2 diabetic patients
- PMID: 24860622
- PMCID: PMC4032353
- DOI: 10.1186/1758-5996-6-56
Effect of single tablet of fixed-dose amlodipine and atorvastatin on blood pressure/lipid control, oxidative stress, and medication adherence in type 2 diabetic patients
Abstract
Background: Oxidized low-density lipoprotein (LDL) plays central roles in the formation and progression of atherosclerotic lesions. Malondialdehyde (MDA)-modified LDL (MDA-LDL) is speculated to be generated as a result of oxidative stress in the human body. Because both amlodipine and atorvastatin have been reported to reduce oxidative stress, it is expected that both drugs would have a favorable influence to reduce oxidative stress.
Objective: The objective of this study was to investigate the effects of a single pill of amlodipine (5 mg)/atorvastatin (10 mg) on oxidative stress, blood pressure/lipid control and adherence to medication in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Methods: This combination tablet was administered to 29 patients (16 male), and MDA-LDL, blood pressure, lipid profile, renal/liver function, CPK, hs-CRP, adiponectin, BNP, and HbA1c were measured at baseline, 6, and 12 months, and baPWV and mean IMT were measured at baseline and 12 months. Medication adherence was examined using a questionnaire at 6 months.
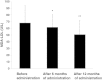
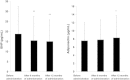
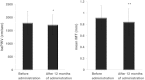
Results: MDA-LDL was decreased significantly. LDL-C, TG, and Cr were significantly decreased at 6 and 12 months compared with baseline. eGFR was increased at 6 months, and urinary albumin/creatinine ratio was decreased at 12 months. BNP was decreased at 6 and 12 months, and adiponectin was increased at 12 months. Both mean IMT and baPWV were significantly decreased. The results of the questionnaire showed that 93% of patients were satisfied with this medication. No severe adverse event was observed.
Conclusion: This combination tablet controlled both hypertension and dyslipidemia well in type 2 diabetic patients. The deceases in mean IMT and baPWV might suggest the improvement of atherosclerosis by this medication, which could be caused by the reduction of oxidative stress measured by MDA-LDL. In addition, this medication is expected to improve medication adherence.
Keywords: Amlodipine; Atherosclerosis; Atorvastatin; Combination tablet; Diabetes mellitus; Dyslipidemia; Hypertension; Malondialdehyde-modified low-density lipoprotein; Medication adherence; Oxidative stress.
Figures
References
-
- Kotani K, Maekawa M, Kanno T, Kondo A, Toda N. Manabe: Distribution of immunoreactive malondialdehyde-modified low-density lipoprotein in human serum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994;17:121–125. - PubMed
-
- Tanaga K, Bujo H, Inoue M, Mikami K, Kotani K, Takahashi K, Kanno T, Saito Y. Increased circulating malondialdehyde-modified LDL levels in patients with coronary artery diseases and their association with peak sizes of LDL particles. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2002;22:662–666. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000012351.63938.84. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

