Vascular Response to Graded Angiotensin II Infusion in Offspring Subjected to High-Salt Drinking Water during Pregnancy: The Effect of Blood Pressure, Heart Rate, Urine Output, Endothelial Permeability, and Gender
- PMID: 24860669
- PMCID: PMC4016930
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/876527
Vascular Response to Graded Angiotensin II Infusion in Offspring Subjected to High-Salt Drinking Water during Pregnancy: The Effect of Blood Pressure, Heart Rate, Urine Output, Endothelial Permeability, and Gender
Abstract
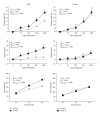
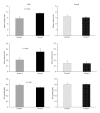
Introduction. Rennin-angiotensin system and salt diet play important roles in blood pressure control. We hypothesized that the high-salt intake during pregnancy influences the degree of angiotensin-dependent control of the blood pressure in adult offspring. Methods. Female Wistar rats in two groups (A and B) were subjected to drink tap and salt water, respectively, during pregnancy. The offspring were divided into four groups as male and female offspring from group A (groups 1 and 2) and from group B (groups 3 and 4). In anesthetized matured offspring mean arterial pressure (MAP), heart rate and urine output were measured in response to angiotensin II (AngII) (0-1000 ng/kg/min, iv) infusion. Results. An increase in MAP was detected in mothers with salt drinking water (P < 0.05). The body weight increased and kidney weight decreased significantly in male offspring from group 3 in comparison to group 1 (P < 0.05). MAP and urine volume in response to AngII infusion increased in group 3 (P < 0.05). These findings were not observed in female rats. Conclusion. Salt overloading during pregnancy had long-term effects on kidney weight and increased sex-dependent response to AngII infusion in offspring (adult) that may reveal the important role of diet during pregnancy in AngII receptors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mineralocorticoid modulation of central angiotensin-induced neuronal activity, water intake and sodium appetite.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2007 May;40(5):699-705. doi: 10.1590/s0100-879x2007000500014. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2007. PMID: 17464433 Review.
-
Renin-angiotensin system function and blood pressure in adult rats after perinatal salt overload.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2003 Jun;13(3):133-9. doi: 10.1016/s0939-4753(03)80172-2. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2003. PMID: 12955794
-
Low birth weight in response to salt restriction during pregnancy is not due to alterations in uterine-placental blood flow or the placental and peripheral renin-angiotensin system.Physiol Behav. 2008 Sep 3;95(1-2):145-51. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2008.05.011. Epub 2008 May 21. Physiol Behav. 2008. PMID: 18572207
-
High salt intake potentiates the renal vascular and glomerular damage caused by low doses of angiotensin II in uni-nephrectomized rats.J Hypertens. 1999 Jul;17(7):923-32. doi: 10.1097/00004872-199917070-00008. J Hypertens. 1999. PMID: 10419065
-
Early changes of hypothalamic angiotensin II receptors expression in gestational protein-restricted offspring: effect on water intake, blood pressure and renal sodium handling.J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2013 Sep;14(3):271-82. doi: 10.1177/1470320312456328. Epub 2012 Aug 30. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2013. PMID: 22936038
Cited by
-
Effect of enalapril in cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats; gender-related difference.Adv Biomed Res. 2016 Jan 29;5:14. doi: 10.4103/2277-9175.175253. eCollection 2016. Adv Biomed Res. 2016. PMID: 26962516 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Maternal c-Src Ameliorates the Male Offspring Hypertension by Suppressing Inflammation and Neurotransmitters in the Paraventricular Nucleus.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2021 Oct;21(10):820-834. doi: 10.1007/s12012-021-09672-z. Epub 2021 Jul 16. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 34269955
-
Cilostazol suppresses angiotensin II-induced apoptosis in endothelial cells.Mol Med Rep. 2016 Mar;13(3):2597-605. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.4881. Epub 2016 Feb 5. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 26862035 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ganzevoort W, Rep A, Bonsel GJ, de Vries JIP, Wolf H. Plasma volume and blood pressure regulation in hypertensive pregnancy. Journal of Hypertension. 2004;22(7):1235–1242. - PubMed
-
- Giardina JB, Cockrell KL, Granger JP, Khalil RA. Low-salt diet enhances vascular reactivity and Ca2+ entry in pregnant rats with normal and reduced uterine perfusion pressure. Hypertension. 2002;39(2, part 2):368–374. - PubMed
-
- Barron LA, Giardina JB, Granger JP, Khalil RA. High-salt diet enhances vascular reactivity in pregnant rats with normal and reduced uterine perfusion pressure. Hypertension. 2001;38(3, part 2):730–735. - PubMed
-
- Kuller LH. Salt and blood pressure: population and individual perspectives. American Journal of Hypertension. 1997;10(5, part 2):29S–36S. - PubMed
-
- Tobian L. Salt and hypertension. Lessons from animal models that relate to human hypertension. Hypertension. 1991;17(1, supplement):I52–I58. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

