ABO-incompatible living-donor pediatric kidney transplantation in Japan
- PMID: 24860855
- PMCID: PMC3884161
- DOI: 10.6061/clinics/2014(sup01)05
ABO-incompatible living-donor pediatric kidney transplantation in Japan
Abstract
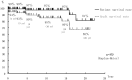
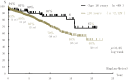
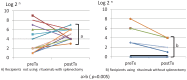
The Japanese ABO-Incompatible Transplantation Committee officially collected and analyzed data on pediatric ABO-incompatible living-donor kidney transplantation in July 2012. The age of a child was defined as <16 years, and 89 children who had undergone ABO-incompatible living-donor kidney transplantation from 1989 to 2011 were entered in a registry. These data were presented as the Japanese registry of pediatric ABO-incompatible living-donor kidney transplantation at the regional meetings of the International Pediatric Transplantation Association (IPTA) in Nagoya in September 2012 and in Sao Paulo in November 2012.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported.
Figures


References
-
- Takahashi K. Rejection in ABO incompatible kidney transplantation- why is hyperacute rejection due to ABO histo-blood group related antigens absent? In: Takahashi K, editor. Abo-Incompatible Kidney Transplantation. Vol. 2011. Amsterdam: Elsevier; pp. 33–40.
-
- Shishido S, Hyodo YY, Aoki Y, Takasu J, Kawamura T, Sakai KK, et al. Outcomes of pediatric ABO-incompatible kidney transplantations are equivalent to ABO-compatible controls. Transplant Proc. 2012;44(1):214–6. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi K, Saito K. ABO incompatible kidney transplantation. Transplant Rev (Orlando) 2013;27(1):1–8. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi K. Why ABO incompatible kidney transplantation has become widely adopted in Japan. In: Takahashi K, editor. Abo-Incompatible Kidney Transplantation. Vol. 2011. Amsterdam: Elsevier; pp. 11–15.
-
- North American Pediatric Renal Trials and Collaborative Studies (NAPRTCS) Rockville MD, editor. 2010 Annual Transplant Report. Available from: https://web.emmes.com/study/ped/annlrept/2010_Report.pdf.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

