Spatial differences and temporal changes in illicit drug use in Europe quantified by wastewater analysis
- PMID: 24861844
- PMCID: PMC4204159
- DOI: 10.1111/add.12570
Spatial differences and temporal changes in illicit drug use in Europe quantified by wastewater analysis
Abstract
Aims: To perform wastewater analyses to assess spatial differences and temporal changes of illicit drug use in a large European population.
Design: Analyses of raw wastewater over a 1-week period in 2012 and 2013.
Setting and participants: Catchment areas of wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) across Europe, as follows: 2012: 25 WWTPs in 11 countries (23 cities, total population 11.50 million); 2013: 47 WWTPs in 21 countries (42 cities, total population 24.74 million).
Measurements: Excretion products of five illicit drugs (cocaine, amphetamine, ecstasy, methamphetamine, cannabis) were quantified in wastewater samples using methods based on liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry.
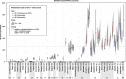
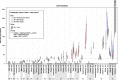
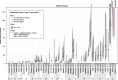
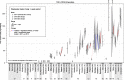
Findings: Spatial differences were assessed and confirmed to vary greatly across European metropolitan areas. In general, results were in agreement with traditional surveillance data, where available. While temporal changes were substantial in individual cities and years (P ranging from insignificant to <10(-3) ), overall means were relatively stable. The overall mean of methamphetamine was an exception (apparent decline in 2012), as it was influenced mainly by four cities.
Conclusions: Wastewater analysis performed across Europe provides complementary evidence on illicit drug consumption and generally concurs with traditional surveillance data. Wastewater analysis can measure total illicit drug use more quickly and regularly than is the current norm for national surveys, and creates estimates where such data does not exist.
Keywords: Amphetamine; cannabis; cocaine; drugs of abuse; ecstasy; methamphetamine; sewage.
© 2014 Society for the Study of Addiction.
Figures

References
-
- European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction. 2008. Assessing Illicit Drugs in Sewage—Potential and Limitations of A New Monitoring Approach. Luxembourg: Office for Official Publications of the European Communities.
-
- Griffiths P, Mounteney J. Drug trend monitoring. In: Miller PG, Strang J, Miller PM, editors. Addiction Research Methods. Oxford, UK: Wiley-Blackwell; 2010. pp. 337–354.
-
- van Nuijs ALN, Castiglioni S, Tarcomnicu I, Postigo C, de Alda ML, Neels H, et al. Illicit drug consumption estimations derived from wastewater analysis: a critical review. Sci Total Environ. 2011;409:3564–3577. - PubMed
-
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) 2013. The challenge of new psychoactive substances. UNODC, Vienna.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

