Determination of meropenem in bacterial media by LC-MS/MS
- PMID: 24861874
- PMCID: PMC4104812
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2014.05.002
Determination of meropenem in bacterial media by LC-MS/MS
Abstract
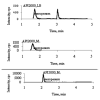
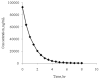
To support the development of a dynamic in vitro human pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic simulation model for biofilm-mediated infections and study stability of meropenem, an LC-MS/MS method for the determination of meropenem in Luria Bertani (LB) media was developed and validated in an API2000 LC-MS/MS system. A partial validation was also performed in M9 media. Sample aliquots of 100μL (or 25μL for M9 media) were mixed with the internal standard (IS) ceftazidime and filtered. The filtrate was directly injected onto a C8 column eluted with ammonium formate (10mM, pH 4) and acetonitrile (0.1% formic acid) in a gradient mode. ESI(+) and MRM with ion pair m/z 384→68 for meropenem and m/z 547→468 for the IS were used for quantification. The calibration curve concentration range was 50 to 25,000ng/mL. The recovery was over 98%. In LB media, significant signal suppression was observed throughout the time period of detection when compared with mobile phase solvents, but the matrix effect was compensated well with the IS. In M9 media, much less signal suppression was observed. The method is simple, fast, and reliable. Using the method, stability of meropenem in LB and M9 media were tested. No significant degradation was observed for at least 8h in both LB media (37°C) and M9 media (30°C), but more than 15% degradation was observed overnight (∼20h). The method was transferred to an API5000 LC-MS/MS system using meropenem-d6 as the IS.
Keywords: LB media; LC–MS/MS; M(9); Meropenem; Stability.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
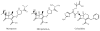
Similar articles
-
Determination of Tobramycin in M9 Medium by LC-MS/MS: Signal Enhancement by Trichloroacetic Acid.J Anal Methods Chem. 2018 Apr 26;2018:7965124. doi: 10.1155/2018/7965124. eCollection 2018. J Anal Methods Chem. 2018. PMID: 29854560 Free PMC article.
-
Measurement of meropenem concentration in different human biological fluids by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2014 Aug;406(20):4997-5007. doi: 10.1007/s00216-014-7910-9. Epub 2014 May 31. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2014. PMID: 24879538
-
Simultaneous determination of bentysrepinine (Y101) and its metabolites M8 and M9 in human plasma by UPLC-MS/MS and its application to a pharmacokinetic study.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018 Feb 20;150:287-293. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2017.12.010. Epub 2017 Dec 13. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018. PMID: 29258048 Clinical Trial.
-
Development and Validation of High-Throughput Bioanalytical Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) Method for the Quantification of Newly Synthesized Antitumor Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors in Human Plasma.Molecules. 2020 Dec 6;25(23):5753. doi: 10.3390/molecules25235753. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33291270 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a bioanalytical method for the simultaneous determination of heroin, its main metabolites, naloxone and naltrexone by LC-MS/MS in human plasma samples: Application to a clinical trial of oral administration of a heroin/naloxone formulation.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2015 Oct 10;114:105-12. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2015.04.044. Epub 2015 May 7. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2015. PMID: 26037158
Cited by
-
Sterilization performance comparison between an autosampler-ready microporous filter vial and a syringe-based filter.J Microbiol Methods. 2019 Sep;164:105669. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2019.105669. Epub 2019 Jul 26. J Microbiol Methods. 2019. PMID: 31356842 Free PMC article.
-
Concentration of meropenem in patients with sepsis and acute kidney injury before and after initiation of continuous renal replacement therapy: a prospective observational trial.Pharmacol Rep. 2020 Feb;72(1):147-155. doi: 10.1007/s43440-019-00056-3. Epub 2020 Jan 4. Pharmacol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32016840
-
Spatiotemporal pharmacodynamics of meropenem- and tobramycin-treated Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2017 Dec 1;72(12):3357-3365. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkx288. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2017. PMID: 28961810 Free PMC article.
-
Meropenem Disposition in Neonatal and Pediatric Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation and Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 May 3;13(5):419. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13050419. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38786147 Free PMC article.
-
New in vitro model to study the effect of human simulated antibiotic concentrations on bacterial biofilms.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Jul;59(7):4074-81. doi: 10.1128/AAC.05037-14. Epub 2015 Apr 27. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 25918138 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhanel GG, Wiebe R, Dilay L, Thomson K, Rubinstein E, Hoban DJ, Noreddin AM, Karlowsky JA. Comparative review of the carbapenems. Drugs. 2007;67:1027–1052. - PubMed
-
- Nicolau DP. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of meropenem. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;47:S32–40. - PubMed
-
- Farin D, Kitzes-Cohen R, Piva G, Gozlan I. High performance Liquid Chromatography Method for the Determination of Meropenem in Human Plasma. Chromatographia. 1999;49:253–255.
-
- Mendez AS, Steppe M, Schapoval EE. Validation of HPLC and UV spectrophotometric methods for the determination of meropenem in pharmaceutical dosage form. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2003;33:947–954. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

