Real-time intraoperative detection of breast cancer using near-infrared fluorescence imaging and Methylene Blue
- PMID: 24862545
- PMCID: PMC4035701
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejso.2014.02.225
Real-time intraoperative detection of breast cancer using near-infrared fluorescence imaging and Methylene Blue
Abstract
Background: Despite recent developments in preoperative breast cancer imaging, intraoperative localization of tumor tissue can be challenging, resulting in tumor-positive resection margins during breast conserving surgery. Based on certain physicochemical similarities between Technetium((99m)Tc)-sestamibi (MIBI), an SPECT radiodiagnostic with a sensitivity of 83-90% to detect breast cancer preoperatively, and the near-infrared (NIR) fluorophore Methylene Blue (MB), we hypothesized that MB might detect breast cancer intraoperatively using NIR fluorescence imaging.
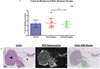
Methods: Twenty-four patients with breast cancer, planned for surgical resection, were included. Patients were divided in 2 administration groups, which differed with respect to the timing of MB administration. N = 12 patients per group were administered 1.0 mg/kg MB intravenously either immediately or 3 h before surgery. The mini-FLARE imaging system was used to identify the NIR fluorescent signal during surgery and on post-resected specimens transferred to the pathology department. Results were confirmed by NIR fluorescence microscopy.
Results: 20/24 (83%) of breast tumors (carcinoma in N = 21 and ductal carcinoma in situ in N = 3) were identified in the resected specimen using NIR fluorescence imaging. Patients with non-detectable tumors were significantly older. No significant relation to receptor status or tumor grade was seen. Overall tumor-to-background ratio (TBR) was 2.4 ± 0.8. There was no significant difference between TBR and background signal between administration groups. In 2/4 patients with positive resection margins, breast cancer tissue identified in the wound bed during surgery would have changed surgical management. Histology confirmed the concordance of fluorescence signal and tumor tissue.
Conclusions: This feasibility study demonstrated an overall breast cancer identification rate using MB of 83%, with real-time intraoperative guidance having the potential to alter patient management.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Image-guided surgery; Methylene Blue; Near-infrared fluorescence imaging.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Quirijn R.J.G. Tummers, M.D.: Nothing to declare
Floris P.R. Verbeek, MSc: Nothing to declare
Boudewijn E. Schaafsma, M.D.: Nothing to declare
Martin C. Boonstra, BSc.: Nothing to declare
Joost R. van der Vorst, M.D.: Nothing to declare
Gerrit-Jan Liefers, M.D., Ph.D.: Nothing to declare
Cornelis J.H. van de Velde, M.D., Ph.D.: Nothing to declare
John V. Frangioni, M.D., Ph.D.: FLARE™ technology is owned by Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, a teaching hospital of Harvard Medical School. Dr. Frangioni has started three for-profit companies, Curadel, Curadel ResVet Imaging, and Curadel Surgical Innovations, which has optioned FLARE™ technology for potential licensing from Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center.
Alexander L. Vahrmeijer, M.D., Ph.D.: Nothing to declare
Figures


References
-
- Hortobagyi GN, de la Garza SJ, Pritchard K, Amadori D, Haidinger R, Hudis CA, Khaled H, Liu MC, Martin M, Namer M, O'Shaughnessy JA, Shen ZZ, Albain KS. The Global Breast Cancer Burden: Variations in Epidemiology and Survival. Clin Breast Cancer. 2005;6(5):391–401. - PubMed
-
- Xu HB, Li L, Xu Q. Tc-99m Sestamibi Scintimammography for the Diagnosis of Breast Cancer: Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression. Nucl Med Commun. 2011;32(11):980–988. - PubMed
-
- Kim SJ, Kim IJ, Bae YT, Kim YK, Kim DS. Comparison of Early and Delayed Quantified Indices of Double-Phase (99m)Tc MIBI Scintimammography in the Detection of Primary Breast Cancer. Acta Radiol. 2005;46(2):148–154. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

