B lymphocytes undergo TLR2-dependent apoptosis upon Shigella infection
- PMID: 24863068
- PMCID: PMC4042640
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20130914
B lymphocytes undergo TLR2-dependent apoptosis upon Shigella infection
Abstract
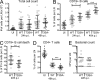
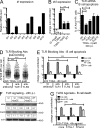
Antibody-mediated immunity to Shigella, the causative agent of bacillary dysentery, requires several episodes of infection to get primed and is short-lasting, suggesting that the B cell response is functionally impaired. We show that upon ex vivo infection of human colonic tissue, invasive S. flexneri interacts with and occasionally invades B lymphocytes. The induction of a type three secretion apparatus (T3SA)-dependent B cell death is observed in the human CL-01 B cell line in vitro, as well as in mouse B lymphocytes in vivo. In addition to cell death occurring in Shigella-invaded CL-01 B lymphocytes, we provide evidence that the T3SA needle tip protein IpaD can induce cell death in noninvaded cells. IpaD binds to and induces B cell apoptosis via TLR2, a signaling receptor thus far considered to result in activation of B lymphocytes. The presence of bacterial co-signals is required to sensitize B cells to apoptosis and to up-regulate tlr2, thus enhancing IpaD binding. Apoptotic B lymphocytes in contact with Shigella-IpaD are detected in rectal biopsies of infected individuals. This study therefore adds direct B lymphocyte targeting to the diversity of mechanisms used by Shigella to dampen the host immune response.
© 2014 Nothelfer et al.
Figures







References
-
- Acosta Rodriguez E.V., Zuniga E.I., Montes C.L., Merino M.C., Bermejo D.A., Amezcua Vesely M.C., Motran C.C., Gruppi A. 2007. Trypanosoma cruzi infection beats the B-cell compartment favouring parasite establishment: can we strike first? Scand. J. Immunol. 66:137–142 10.1111/j.1365-3083.2007.01968.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ahmed F., Clemens J.D., Rao M.R., Sack D.A., Khan M.R., Haque E. 1992. Community-based evaluation of the effect of breast-feeding on the risk of microbiologically confirmed or clinically presumptive shigellosis in Bangladeshi children. Pediatrics. 90:406–411 - PubMed
-
- Bhunia A.K., Feng X. 1999. Examination of cytopathic effect and apoptosis in Listeria monocytogenes-infected hybridoma B-lymphocyte (Ped-2E9) line in vitro. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 9:398–403
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

