FOXO transcription factors: their clinical significance and regulation
- PMID: 24864265
- PMCID: PMC4016844
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/925350
FOXO transcription factors: their clinical significance and regulation
Abstract
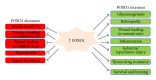
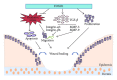
Members of the class O of forkhead box transcription factors (FOXO) have important roles in metabolism, cellular proliferation, stress resistance, and apoptosis. The activity of FOXOs is tightly regulated by posttranslational modification, including phosphorylation, acetylation, and ubiquitylation. Activation of cell survival pathways such as phosphoinositide-3-kinase/AKT/IKK or RAS/mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylates FOXOs at different sites which regulate FOXOs nuclear localization or degradation. FOXO transcription factors are upregulated in a number of cell types including hepatocytes, fibroblasts, osteoblasts, keratinocytes, endothelial cells, pericytes, and cardiac myocytes. They are involved in a number of pathologic and physiologic processes that include proliferation, apoptosis, autophagy, metabolism, inflammation, cytokine expression, immunity, differentiation, and resistance to oxidative stress. These processes impact a number of clinical conditions such as carcinogenesis, diabetes, diabetic complications, cardiovascular disease, host response, and wound healing. In this paper, we focus on the potential role of FOXOs in different disease models and the regulation of FOXOs by various stimuli.
Figures

References
-
- Obsil T, Obsilova V. Structure/function relationships underlying regulation of FOXO transcription factors. Oncogene. 2008;27(16):2263–2275. - PubMed
-
- Van Der Vos KE, Coffer PJ. The extending network of FOXO transcriptional target genes. Antioxidants and Redox Signaling. 2011;14(4):579–592. - PubMed
-
- Lin L, Hron JD, Peng SL. Regulation of NF-κB, Th activation, and autoinflammation by the Forkhead transcription factor Foxo3a. Immunity. 2004;21(2):203–213. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

