Positron emission tomography image-guided drug delivery: current status and future perspectives
- PMID: 24865108
- PMCID: PMC4218872
- DOI: 10.1021/mp500173s
Positron emission tomography image-guided drug delivery: current status and future perspectives
Abstract
Positron emission tomography (PET) is an important modality in the field of molecular imaging, which is gradually impacting patient care by providing safe, fast, and reliable techniques that help to alter the course of patient care by revealing invasive, de facto procedures to be unnecessary or rendering them obsolete. Also, PET provides a key connection between the molecular mechanisms involved in the pathophysiology of disease and the according targeted therapies. Recently, PET imaging is also gaining ground in the field of drug delivery. Current drug delivery research is focused on developing novel drug delivery systems with emphasis on precise targeting, accurate dose delivery, and minimal toxicity in order to achieve maximum therapeutic efficacy. At the intersection between PET imaging and controlled drug delivery, interest has grown in combining both these paradigms into clinically effective formulations. PET image-guided drug delivery has great potential to revolutionize patient care by in vivo assessment of drug biodistribution and accumulation at the target site and real-time monitoring of the therapeutic outcome. The expected end point of this approach is to provide fundamental support for the optimization of innovative diagnostic and therapeutic strategies that could contribute to emerging concepts in the field of "personalized medicine". This review focuses on the recent developments in PET image-guided drug delivery and discusses intriguing opportunities for future development. The preclinical data reported to date are quite promising, and it is evident that such strategies in cancer management hold promise for clinically translatable advances that can positively impact the overall diagnostic and therapeutic processes and result in enhanced quality of life for cancer patients.
Keywords: cancer; image-guided drug delivery; molecular imaging; personalized medicine; positron emission tomography; theranostics.
Figures
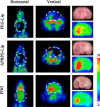
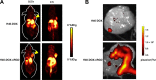
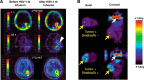
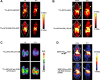
Comment in
-
Optimizing Clinical Drug Product Performance: Applying Biopharmaceutics Risk Assessment Roadmap (BioRAM) and the BioRAM Scoring Grid.J Pharm Sci. 2016 Nov;105(11):3243-3255. doi: 10.1016/j.xphs.2016.07.024. Epub 2016 Sep 19. J Pharm Sci. 2016. PMID: 27659159
Similar articles
-
Targeted multifunctional lipid-based nanocarriers for image-guided drug delivery.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2007 Jul;7(4):425-40. doi: 10.2174/187152007781058613. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2007. PMID: 17630918 Review.
-
Image guided therapy: the advent of theranostic agents.J Control Release. 2012 Jul 20;161(2):328-37. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2012.05.028. Epub 2012 May 22. J Control Release. 2012. PMID: 22626940 Review.
-
Companion Diagnostic 64Cu-Liposome Positron Emission Tomography Enables Characterization of Drug Delivery to Tumors and Predicts Response to Cancer Nanomedicines.Theranostics. 2018 Mar 21;8(9):2300-2312. doi: 10.7150/thno.21670. eCollection 2018. Theranostics. 2018. PMID: 29721081 Free PMC article.
-
Nanotheranostics and image-guided drug delivery: current concepts and future directions.Mol Pharm. 2010 Dec 6;7(6):1899-912. doi: 10.1021/mp100228v. Epub 2010 Oct 6. Mol Pharm. 2010. PMID: 20822168 Review.
-
Tumor Targeting Using Radiolabeled Antibodies for Image-Guided Drug Delivery.Curr Drug Targets. 2015;16(6):625-33. doi: 10.2174/1389450115666141029234200. Curr Drug Targets. 2015. PMID: 25355181 Review.
Cited by
-
A Scalable Method for Squalenoylation and Assembly of Multifunctional 64Cu-Labeled Squalenoylated Gemcitabine Nanoparticles.Nanotheranostics. 2018 Sep 5;2(4):387-402. doi: 10.7150/ntno.26969. eCollection 2018. Nanotheranostics. 2018. PMID: 30324084 Free PMC article.
-
Bioimaging predictors of rilpivirine biodistribution and antiretroviral activities.Biomaterials. 2018 Dec;185:174-193. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.09.018. Epub 2018 Sep 14. Biomaterials. 2018. PMID: 30245386 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Advanced Imaging Modalities in Veterinary Medicine: A Review.Vet Med (Auckl). 2022 May 31;13:117-130. doi: 10.2147/VMRR.S367040. eCollection 2022. Vet Med (Auckl). 2022. PMID: 35669942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Image-Guided Drug Delivery with Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography: A Review of Literature.Curr Drug Targets. 2015;16(6):592-609. doi: 10.2174/1389450115666140902125657. Curr Drug Targets. 2015. PMID: 25182469 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear Nanomedicines: Utilization of Radiolabelling Strategies, Drug Formulation, Delivery, and Regulatory Aspects for Disease Management.Curr Radiopharm. 2025;18(4):262-282. doi: 10.2174/0118744710373025250423042401. Curr Radiopharm. 2025. PMID: 40304320 Review.
References
-
- Hatefi A.; Minko T. Advances in image-guided drug delivery. Drug Delivery Transl. Res. 2012, 2, 1–2. - PubMed
-
- Gaidamakova E. K.; Backer M. V.; Backer J. M. Molecular vehicle for target-mediated delivery of therapeutics and diagnostics. J. Controlled Release 2001, 74, 341–7. - PubMed
-
- MacKay J. A.; Li Z. Theranostic agents that co-deliver therapeutic and imaging agents?. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2010, 62, 1003–4. - PubMed
-
- Chow E. K.; Ho D. Cancer nanomedicine: from drug delivery to imaging. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 216rv4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

