Sertraline induces endoplasmic reticulum stress in hepatic cells
- PMID: 24865413
- PMCID: PMC5736318
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tox.2014.05.007
Sertraline induces endoplasmic reticulum stress in hepatic cells
Abstract
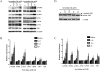
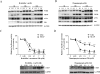
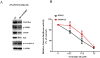
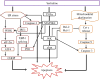
Sertraline is used for the treatment of depression, and is also used for the treatment of panic, obsessive-compulsive, and post-traumatic stress disorders. Previously, we have demonstrated that sertraline caused hepatic cytotoxicity, with mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis being underlying mechanisms. In this study, we used microarray and other biochemical and molecular analyses to identify endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress as a novel molecular mechanism. HepG2 cells were exposed to sertraline and subjected to whole genome gene expression microarray analysis. Pathway analysis revealed that ER stress is among the significantly affected biological changes. We confirmed the increased expression of ER stress makers by real-time PCR and Western blots. The expression of typical ER stress markers such as PERK, IRE1α, and CHOP was significantly increased. To study better ER stress-mediated drug-induced liver toxicity; we established in vitro systems for monitoring ER stress quantitatively and efficiently, using Gaussia luciferase (Gluc) and secreted alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) as ER stress reporters. These in vitro systems were validated using well-known ER stress inducers. In these two reporter assays, sertraline inhibited the secretion of Gluc and SEAP. Moreover, we demonstrated that sertraline-induced apoptosis was coupled to ER stress and that the apoptotic effect was attenuated by 4-phenylbutyrate, a potent ER stress inhibitor. In addition, we showed that the MAP4K4-JNK signaling pathway contributed to the process of sertraline-induced ER stress. In summary, we demonstrated that ER stress is a mechanism of sertraline-induced liver toxicity.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Drug-induced liver toxicity; Endoplasmic reticulum stress; MAPK pathway; Reporter gene assay; Sertraline.
Published by Elsevier Ireland Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

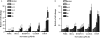

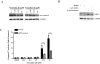
Similar articles
-
A mechanism of perhexiline's cytotoxicity in hepatic cells involves endoplasmic reticulum stress and p38 signaling pathway.Chem Biol Interact. 2021 Jan 25;334:109353. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2020.109353. Epub 2020 Dec 9. Chem Biol Interact. 2021. PMID: 33309543 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress and MAPK signaling pathway activation underlie leflunomide-induced toxicity in HepG2 Cells.Toxicology. 2017 Dec 1;392:11-21. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2017.10.002. Epub 2017 Oct 5. Toxicology. 2017. PMID: 28988120 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Induction and ERK1/2 Activation Contribute to Nefazodone-Induced Toxicity in Hepatic Cells.Toxicol Sci. 2016 Dec;154(2):368-380. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfw173. Epub 2016 Sep 9. Toxicol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27613715 Free PMC article.
-
PPARγ-inactive Δ2-troglitazone independently triggers ER stress and apoptosis in breast cancer cells.Mol Carcinog. 2015 May;54(5):393-404. doi: 10.1002/mc.22109. Epub 2013 Nov 30. Mol Carcinog. 2015. PMID: 24293218
-
Secreted blood reporters: insights and applications.Biotechnol Adv. 2011 Nov-Dec;29(6):997-1003. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2011.08.021. Epub 2011 Sep 8. Biotechnol Adv. 2011. PMID: 21920429 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress eIF2α-ATF4 pathway-mediated cyclooxygenase-2 induction regulates cadmium-induced autophagy in kidney.Cell Death Dis. 2016 Jun 2;7(6):e2251. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.78. Cell Death Dis. 2016. PMID: 27253415 Free PMC article.
-
Species translatable blood gene signature as a marker of exposure to smoking: computational approaches of the top ranked teams in the sbv IMPROVER Systems Toxicology challenge.Comput Toxicol. 2018 Feb;5:25-30. doi: 10.1016/j.comtox.2017.04.001. Epub 2017 Apr 28. Comput Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 29556587 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction induced by leflunomide and its active metabolite.Toxicology. 2018 Mar 1;396-397:33-45. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2018.02.003. Epub 2018 Feb 8. Toxicology. 2018. PMID: 29427785 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of metabolomics and transcriptomics in nanotoxicity studies.BMB Rep. 2018 Jan;51(1):14-20. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2018.51.1.237. BMB Rep. 2018. PMID: 29301609 Free PMC article.
-
Reactive oxygen species and c-Jun N-terminal kinases contribute to TEMPO-induced apoptosis in L5178Y cells.Chem Biol Interact. 2015 Jun 25;235:27-36. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2015.04.009. Epub 2015 Apr 13. Chem Biol Interact. 2015. PMID: 25882087 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Apostolova N, Gomez-Sucerquia LJ, Alegre F, et al. ER stress in human hepatic cells treated with Efavirenz: mitochondria again. J. Hepatol. 2013;59(4):780–789. - PubMed
-
- Berger J, Hauber J, Hauber R, Geiger R, Cullen BR. Secreted placental alkaline phosphatase: a powerful new quantitative indicator of gene expression in eukaryotic cells. Gene. 1988;66(1):1–10. - PubMed
-
- Carvajal Garcia-Pando A, Garcia del Pozo J, Sanchez AS, Velasco MA, Rueda de Castro AM, Lucena MI. Hepatotoxicity associated with the new antidepressants. J. Clin. Psychiatry. 2002;63(2):135–137. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

