Schizophrenia-risk variant rs6994992 in the neuregulin-1 gene on brain developmental trajectories in typically developing children
- PMID: 24865593
- PMCID: PMC4035723
- DOI: 10.1038/tp.2014.41
Schizophrenia-risk variant rs6994992 in the neuregulin-1 gene on brain developmental trajectories in typically developing children
Abstract
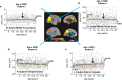
The neuregulin-1 (NRG1) gene is one of the best-validated risk genes for schizophrenia, and psychotic and bipolar disorders. The rs6994992 variant in the NRG1 promoter (SNP8NRG243177) is associated with altered frontal and temporal brain macrostructures and/or altered white matter density and integrity in schizophrenic adults, as well as healthy adults and neonates. However, the ages when these changes begin and whether neuroimaging phenotypes are associated with cognitive performance are not fully understood. Therefore, we investigated the association of the rs6994992 variant on developmental trajectories of brain macro- and microstructures, and their relationship with cognitive performance. A total of 972 healthy children aged 3-20 years had the genotype available for the NRG1-rs6994992 variant, and were evaluated with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and neuropsychological tests. Age-by-NRG1-rs6994992 interactions and genotype effects were assessed using a general additive model regression methodology, covaried for scanner type, socioeconomic status, sex and genetic ancestry factors. Compared with the C-carriers, children with the TT-risk-alleles had subtle microscopic and macroscopic changes in brain development that emerge or reverse during adolescence, a period when many psychiatric disorders are manifested. TT-children at late adolescence showed a lower age-dependent forniceal volume and lower fractional anisotropy; however, both measures were associated with better episodic memory performance. To our knowledge, we provide the first multimodal imaging evidence that genetic variation in NRG1 is associated with age-related changes on brain development during typical childhood and adolescence, and delineated the altered patterns of development in multiple brain regions in children with the T-risk allele(s).
Figures



Similar articles
-
A functional neuregulin-1 gene variant and stressful life events: Effect on drug use in a longitudinal population-representative cohort study.J Psychopharmacol. 2017 Jan;31(1):54-61. doi: 10.1177/0269881116655979. Epub 2016 Jul 10. J Psychopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27353026
-
Neuregulin 1 (8p12) and childhood-onset schizophrenia: susceptibility haplotypes for diagnosis and brain developmental trajectories.Mol Psychiatry. 2007 Feb;12(2):195-205. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4001906. Epub 2006 Oct 10. Mol Psychiatry. 2007. PMID: 17033632
-
Neuregulin-1 (NRG1) polymorphisms linked with psychosis transition are associated with enlarged lateral ventricles and white matter disruption in schizophrenia.Psychol Med. 2018 Apr;48(5):801-809. doi: 10.1017/S0033291717002173. Epub 2017 Aug 22. Psychol Med. 2018. PMID: 28826413
-
Genetic risk for white matter abnormalities in bipolar disorder.Int Rev Psychiatry. 2009;21(4):387-93. doi: 10.1080/09540260902962180. Int Rev Psychiatry. 2009. PMID: 20374152 Review.
-
Neuregulin 1 and schizophrenia: genetics, gene expression, and neurobiology.Biol Psychiatry. 2006 Jul 15;60(2):132-40. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2005.11.002. Epub 2006 Jan 25. Biol Psychiatry. 2006. PMID: 16442083 Review.
Cited by
-
Lifetime surgical exposure, episodic memory, and forniceal microstructure in older adults.J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 2019 Dec;41(10):1048-1059. doi: 10.1080/13803395.2019.1647151. Epub 2019 Aug 1. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 2019. PMID: 31370773 Free PMC article.
-
ERBB4 polymorphism and family history of psychiatric disorders on age-related cortical changes in healthy children.Brain Imaging Behav. 2015 Mar;9(1):128-40. doi: 10.1007/s11682-015-9363-y. Brain Imaging Behav. 2015. PMID: 25744101 Free PMC article.
-
Dyslexia and language impairment associated genetic markers influence cortical thickness and white matter in typically developing children.Brain Imaging Behav. 2016 Mar;10(1):272-82. doi: 10.1007/s11682-015-9392-6. Brain Imaging Behav. 2016. PMID: 25953057 Free PMC article.
-
Disruptions in white matter microstructure associated with impaired visual associative memory in schizophrenia-spectrum illness.Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2022 Sep;272(6):971-983. doi: 10.1007/s00406-021-01333-0. Epub 2021 Sep 24. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 34557990
-
Fornix as an imaging marker for episodic memory deficits in healthy aging and in various neurological disorders.Front Aging Neurosci. 2015 Jan 14;6:343. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2014.00343. eCollection 2014. Front Aging Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25642186 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Steinthorsdottir V, Stefansson H, Ghosh S, Birgisdottir B, Bjornsdottir S, Fasquel AC, et al. Multiple novel transcription initiation sites for NRG1. Gene. 2004;342:97–105. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

