A cluster randomized controlled trial to reduce childhood diarrhea using hollow fiber water filter and/or hygiene-sanitation educational interventions
- PMID: 24865680
- PMCID: PMC4080561
- DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.13-0568
A cluster randomized controlled trial to reduce childhood diarrhea using hollow fiber water filter and/or hygiene-sanitation educational interventions
Abstract
Safe domestic potable water supplies are urgently needed to reduce childhood diarrheal disease. In periurban neighborhoods in Cochabamba, Bolivia, we conducted a cluster randomized controlled trial to evaluate the efficacy of a household-level hollow fiber filter and/or behavior change communication (BCC) on water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH) to reduce the diarrheal disease in children less than 5 years of age. In total, 952 households were followed for a period of 12 weeks post-distribution of the study interventions. Households using Sawyer PointONE filters had significantly less diarrheal disease compared with the control arm during the intervention period, which was shown by diarrheal prevalence ratios of 0.21 (95% confidence interval [95% CI] = 0.15-0.30) for the filter arm and 0.27 (95% CI = 0.22-0.34) for the filter and WASH BCC arm. A non-significant reduction in diarrhea prevalence was reported in the WASH BCC study arm households (0.71, 95% CI = 0.59-0.86).
© The American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene.
Figures

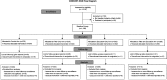
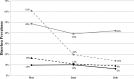
Similar articles
-
Reducing diarrhea through the use of household-based ceramic water filters: a randomized, controlled trial in rural Bolivia.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2004 Jun;70(6):651-7. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2004. PMID: 15211008 Clinical Trial.
-
Modeling the Impact of Population Intervention Strategies on Reducing Health Disparities: Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene Interventions and Childhood Diarrheal Disease in Peru.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2021 Jan;104(1):338-345. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.19-0775. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2021. PMID: 33236711 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of school water, sanitation, and hygiene interventions on the health of younger siblings of pupils: a cluster-randomized trial in Kenya.Am J Public Health. 2014 Jan;104(1):e91-7. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2013.301412. Epub 2013 Nov 14. Am J Public Health. 2014. PMID: 24228683 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Water, sanitation and hygiene in developing countries: interventions and diarrhoea--a review.Water Sci Technol. 2005;52(8):133-42. Water Sci Technol. 2005. PMID: 16312960 Review.
-
Impact on childhood mortality of interventions to improve drinking water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH) to households: Systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS Med. 2023 Apr 20;20(4):e1004215. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1004215. eCollection 2023 Apr. PLoS Med. 2023. PMID: 37079510 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Risk factors for diarrhea in children under five years of age residing in peri-urban communities in Cochabamba, Bolivia.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2014 Dec;91(6):1190-6. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.14-0057. Epub 2014 Oct 13. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2014. PMID: 25311693 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Water, sanitation and hygiene interventions for acute childhood diarrhea: a systematic review to provide estimates for the Lives Saved Tool.BMC Public Health. 2017 Nov 7;17(Suppl 4):776. doi: 10.1186/s12889-017-4746-1. BMC Public Health. 2017. PMID: 29143638 Free PMC article.
-
Care Groups II: A Summary of the Child Survival Outcomes Achieved Using Volunteer Community Health Workers in Resource-Constrained Settings.Glob Health Sci Pract. 2015 Sep 15;3(3):370-81. doi: 10.9745/GHSP-D-15-00052. Print 2015 Sep. Glob Health Sci Pract. 2015. PMID: 26374799 Free PMC article.
-
Effective community-based interventions to prevent and control infectious diseases in urban informal settlements in low- and middle-income countries: a systematic review.Syst Rev. 2024 Oct 4;13(1):253. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02651-9. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39367477 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions to improve sanitation for preventing diarrhoea.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jan 25;1(1):CD013328. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013328.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36697370 Free PMC article.
References
-
- United Nations Children's Fund and World Health Organization . Progress on Drinking Water and Sanitation: 2012 Update. New York, NY: United Nations Children's Fund; 2012.
-
- United Nations The Millennium Development Goals Report 2012. 2012. http://www.un.org/millenniumgoals/pdf/MDG%20Report%202012.pdf Available at. Accessed September 28, 2013.
-
- Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Global Burden of Disease Study 2010 (GBD 2010) Results by Risk Factor 1990–2010. Seattle, WA: Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME); 2012.
-
- World Health Organization . GLAAS 2010: UN-Water Global Annual Assessment of Sanitation and Drinking-Water: Targeting Resources for Better Results. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2010.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

