Detecting a weak association by testing its multiple perturbations: a data mining approach
- PMID: 24866319
- PMCID: PMC4035575
- DOI: 10.1038/srep05081
Detecting a weak association by testing its multiple perturbations: a data mining approach
Abstract
Many risk factors/interventions in epidemiologic/biomedical studies are of minuscule effects. To detect such weak associations, one needs a study with a very large sample size (the number of subjects, n). The n of a study can be increased but unfortunately only to an extent. Here, we propose a novel method which hinges on increasing sample size in a different direction-the total number of variables (p). We construct a p-based 'multiple perturbation test', and conduct power calculations and computer simulations to show that it can achieve a very high power to detect weak associations when p can be made very large. As a demonstration, we apply the method to analyze a genome-wide association study on age-related macular degeneration and identify two novel genetic variants that are significantly associated with the disease. The p-based method may set a stage for a new paradigm of statistical tests.
Figures

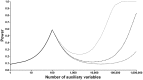
Similar articles
-
Genotype distribution-based inference of collective effects in genome-wide association studies: insights to age-related macular degeneration disease mechanism.BMC Genomics. 2016 Aug 30;17(1):695. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2871-3. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27576376 Free PMC article.
-
Gene-based association analysis for bivariate time-to-event data through functional regression with copula models.Biometrics. 2020 Jun;76(2):619-629. doi: 10.1111/biom.13165. Epub 2019 Nov 14. Biometrics. 2020. PMID: 31625595 Free PMC article.
-
AprioriGWAS, a new pattern mining strategy for detecting genetic variants associated with disease through interaction effects.PLoS Comput Biol. 2014 Jun 5;10(6):e1003627. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003627. eCollection 2014 Jun. PLoS Comput Biol. 2014. PMID: 24901472 Free PMC article.
-
Highly penetrant alleles in age-related macular degeneration.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2014 Nov 6;5(3):a017202. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a017202. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2014. PMID: 25377141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Age-related macular degeneration: genetics and biology coming together.Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2014;15:151-71. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genom-090413-025610. Epub 2014 Apr 16. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2014. PMID: 24773320 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A test for treatment effects in randomized controlled trials, harnessing the power of ultrahigh dimensional big data.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Oct;98(43):e17630. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000017630. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31651877 Free PMC article.
-
Health outcome prediction using multiple perturbations.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Jan;99(2):e18664. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000018664. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 31914054 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siontis G. C. & Ioannidis J. P. Risk factors and interventions with statistically significant tiny effects. Int. J. Epidemiol. 40, 1292–1307 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Ioannidis J. P., Trikalinos T. A. & Khoury M. J. Implications of small effect sizes of individual genetic variants on the design and interpretation of genetic association studies of complex diseases. Am. J. Epidemiol. 164, 609–614 (2006). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

