The declining demand for hospital care as a rationale for duty hour reform
- PMID: 24866469
- PMCID: PMC4175648
- DOI: 10.1007/s11606-014-2901-2
The declining demand for hospital care as a rationale for duty hour reform
Abstract
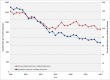
The regulation of duty hours of physicians in training remains among the most hotly debated subjects in medical education. Although recent duty hour reforms have been chiefly motivated by concerns about resident well-being and medical errors attributable to resident fatigue, the debate surrounding duty hour reform has infrequently involved discussion of one of the most important secular changes in hospital care that has affected nearly all developed countries over the last 3 decades: the declining demand for hospital care. For example, in 1980, we show that resident physicians in US teaching hospitals provided, on average, 1,302 inpatient days of care per resident physician compared to 593 inpatient days in 2011, a decline of 54%. This decline in the demand for hospital care by residents provides an under-recognized economic rationale for reducing residency duty hours, a rationale based solely on supply and demand considerations. Work hour reductions and growing requirements for outpatient training can be seen as an appropriate response to the shrinking demand for hospital care across the health-care sector.
Figures
References
-
- Moonesinghe SR, Lowery J, Shahi N, Millen A, Beard JD. Impact of reduction in working hours for doctors in training on postgraduate medical education and patients’ outcomes: systematic review. BMJ 342:d1580 http://www.bmj.com/content/342/bmj.d1580. - PubMed
-
- Buysse DJ, Barzansky B, Dinges D, et al. Sleep, fatigue, and medical training: setting an agenda for optimal learning and patient care. Sleep. 2003;26:218–225. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources